Chapter: Medical Physiology: Urine Formation by the Kidneys: II. Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
Distal Tubule
Distal Tubule
The thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle empties into the distal tubule. The very first portion of the distal tubule forms part of the juxta-glomerular complex that provides feedback control ofGFR and blood flow in this same nephron. The next part of the distal tubule is highly convoluted and has many of the same reabsorptive characteristics of the thick segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. That is, it avidly reabsorbs most of the ions, including sodium, potassium, and chloride, but is vir-tually impermeable to water and urea. For this reason, it is referred to as the diluting segment because it also dilutes the tubular fluid.
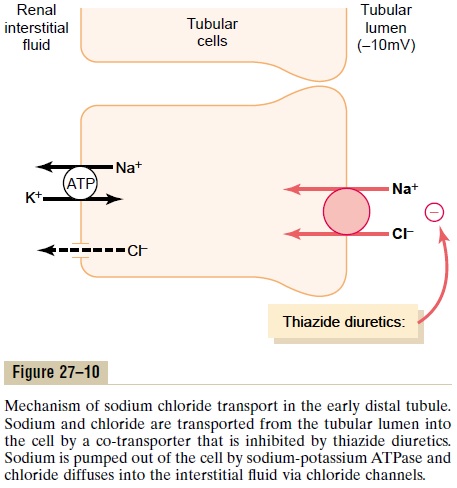
Approximately 5 percent of the filtered load of sodium chloride is reabsorbed in the early distal tubule. The sodium-chloride co-transporter moves sodium chloride from the tubular lumen into the cell, and the sodium-potassium ATPase pump transports sodium out of the cell across the basolateral mem-brane (Figure 27–10). Chloride diffuses out of the cell into the renal interstitial fluid through chloride chan-nels in the basolateral membrane. The thiazide diuret-ics, which are widely used to treat disorders such ashypertension and heart failure, inhibit the sodium-chloride co-transporter.
Related Topics