Chapter: Medical Physiology: Regulation of Acid-Base Balance
Complex Acid-Base Disorders and Use of the Acid-Base Nomogram for Diagnosis
Complex Acid-Base Disorders and Use of the Acid-Base Nomogram for Diagnosis
In some instances, acid-base disorders are not accompanied by appropriate compensatory responses. When this occurs, the abnormality is referred to as a mixedacid-base disorder. This means that there are two ormore underlying causes for the acid-base disturbance. For example, a patient with low pH would be catego-rized as acidotic. If the disorder was metabolically medi-ated, this would also be accompanied by a low plasma HCO3– concentration and, after appropriate respiratory compensation, a low PCO2. However, if the low plasma pH and low HCO3– concentration are associated with elevated PCO2, one would suspect a respiratory compo-nent to the acidosis as well as a metabolic component. Therefore, this disorder would be categorized as a mixed acidosis. This could occur, for example, in a patient with acute HCO3– loss from the gastrointestinal tract because of diarrhea (metabolic acidosis) who also has emphysema (respiratory acidosis).
A convenient way to diagnose acid-base disorders is to use an acid-base nomogram, as shown in Figure 30–11. This diagram can be used to determine the type of acidosis or alkalosis, as well as its severity. In this acid-base diagram, pH, HCO3– concentration, and PCO2 values intersect according to the Henderson-Hassel-balch equation. The central open circle shows normal values and the deviations that can still be considered within the normal range. The shaded areas of the diagram show the 95 per cent confidence limits for the normal compensations to simple metabolic and respira-tory disorders.
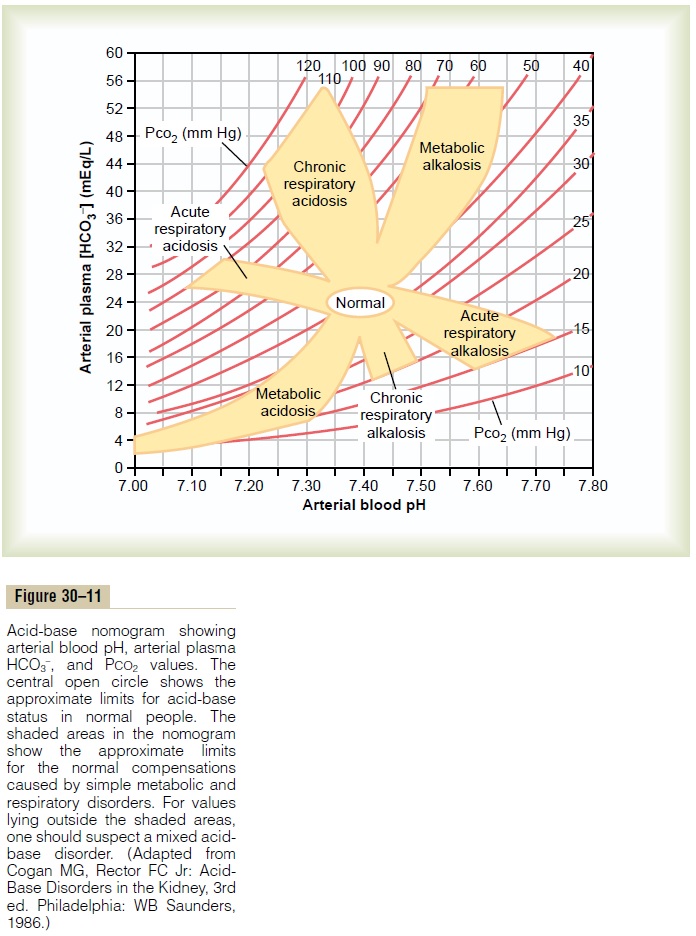
When using this diagram, one must assume that suf-ficient time has elapsed for a full compensatory response, which is 6 to 12 hours for the ventilatory com-pensations in primary metabolic disorders and 3 to 5 days for the metabolic compensations in primary respi-ratory disorders. If a value is within the shaded area, this suggests that there is a simple acid-base disturbance. Conversely, if the values for pH, bicarbonate, or PCO2 lie outside the shaded area, this suggests that there may be a mixed acid-base disorder.
It is important to recognize that an acid-base value within the shaded area does not always mean that there is a simple acid-base disorder. With this reservation in mind, the acid-base diagrams can be used as a quick means of determining the specific type and severity of an acid-base disorder.
For example, assume that the arterial plasma from a patient yields the following values: pH 7.30, plasma HCO3– concentration 12.0 mEq/L, and plasma PCO2 25 mm Hg. With these values, one can look at the diagram and find that this represents a simple metabolic acidosis, with appropriate respiratory compensation that reduces the PCO2 from its normal value of 40 mm Hg to 25 mm Hg.
A second example would be a patient with the fol-lowing values: pH 7.15, plasma HCO3– concentration 7 mEq/L, and plasma PCO250 mm Hg. In this example, the patient is acidotic, and there appears to be a meta-bolic component because the plasma HCO3–concentra-tion is lower than the normal value of 24 mEq/L. However, the respiratory compensation that would normally reduce PCO2is absent, and PCO2 is slightly increased above the normal value of 40 mm Hg. This is
The acid-base diagram serves as a quick way to assess the type and severity of disorders that may be con-tributing to abnormal pH, PCO2 , and plasma bicarbon-ate concentrations. In a clinical setting, the patient’s history and other physical findings also provide impor-tant clues concerning causes and treatment of the acid-base disorders.
Related Topics