Chapter: Modern Medical Toxicology: Neurotoxic Poisons: Stimulants
Cocaine: Autopsy Features, Mediocosocial and Forensic Issues - Stimulant Neurotoxic Poisons
Autopsy Features
·
There are no specific findings at
autopsy, except for nasal septal ulceration and perforation if the deceased had
been a long-term abuser of cocaine. Histological study of nasal septal mucosa
in such cases may reveal characteristic changes including arteriolar
thickening, increased perivas- cular deposition of collagen and glycoprotein,
and chronic inflammatory cellular infiltration.
·
Histopathology of heart may
demonstrate microfocal lymphocytic infiltrates, acute coronary thrombosis,
early coagulation necrosis of myocardial fibres, and non-atherosclerotic
coronary obstruction due to intimal proliferation.
·
Cocaine can be recovered by sampling
from recent injec- tion sites, or by swabs from the nasal mucosa. It can also
be recovered from the liver and especially brain, where cocaine may be found
not only in dopamine-rich areas such as caudate, putamen, and nucleus
accumbens, but also in other extra-striatal regions.
·
Specimens obtained postmortem should
be preserved with sodium fluoride, refrigerated, and analysed quickly. Tissue
specimens should be frozen.
Mediocosocial and Forensic Issues
·
Cocaine has been abused for
centuries, but its toxic proper- ties have been studied extensively only in the
last couple of decades. In the current drug subculture, cocaine has become the
“champagne drug” because of its cost
and relative scarcity. The situation is not much different in India with
cocaine abuse restricted mainly to the affluent classes of society.
· Cocaine has always been popular with musicians (espe- cially jazz and rock), other artistes, and film personalities. Today cocaine has made inroads into the general popula- tion, especially adolescents. After the cocaine epidemic of the 1970s (“snorting seventies”) in the West, there had been a relative lull in the 1980s and early 1990s. A recent survey shows the cocaine resurgence of the 21st century has not only affected Western countries, but even poorer countries such as India. In fact a sizeable chunk of youth (including girls) from well-to-do families in metropolitan cities such as Mumbai, Delhi, and Bangalore have no qualms about drug abuse, and even openly admit to using “party drugs” such as cocaine as a “cool” mode of recreation. Since cocaine has a reputation of enhancing sexual pleasure, such wide- spread abuse has also led to increased spread of sexually transmitted diseases such as AIDS because of high-risk sexual practices among the users.
·
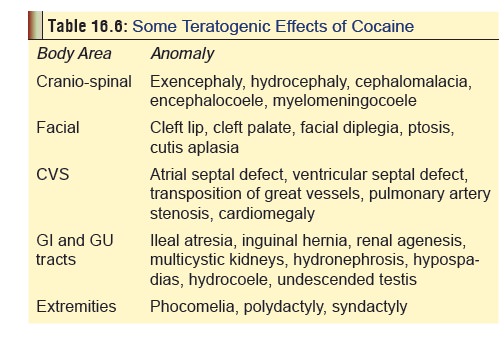
Cocaine abuse by pregnant mothers
can lead to devastating effects on the foetus and the new-born (Table 16.5). There is convincing
evidence that cocaine is teratogenic and can play an important role in the
causation of several serious congenital anomalies (Table 16.6).

·
Cocaine abuse is well-known for its
propensity to cause sudden death not only due to its deleterious effects on
health (cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, malignant
hyperthermia, renal failure), but also due to its capacity to provoke the user
to commit acts of aggression and violence. Deaths due to massive overdose are
especially common among those who smuggle the drug within their bodies
(“cocaine packers”).
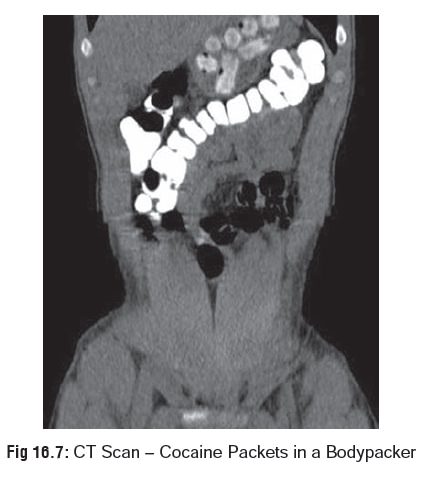
Bodypacker Syndrome:
–– The practice of swallowing balloons, condoms,
or plastic packets filled with illegal drugs for the purpose of smuggling is
called “body packing”, (Fig 16.7),
and the individual who does this is referred to as a “mule”.
–– This must be differentiated from “body
stuffing” in which an individual who is on the verge of being arrested for
possession of illegal drugs, swallows his illicit contraband to conceal the
evidence. Leaking from these poorly wrapped packets can produce cocaine
toxicity.
–– Sudden death due to massive overdose can occur in either a bodypacker or a bodystuffer, if one or more of the ingested packages burst within the gastrointestinal tract.
––
Diagnosis
–– Treatment:
--Emesis,
lavage, charcoal, as applicable.
--Cathartic/whole
bowel irrigation to flush the packages out of the intestines.
--Symptomatic
patients should be considered a medical emergency, and be evaluated for
surgical removal of the packets.
--Asymptomatic
patients should be monitored in an intensive care unit until the cocaine packs
have been eliminated. This must be confirmed by follow-up plain radiography and
barium swallows.
--Bowel
obstruction in asymptomatic patients may necessitate surgery. Endoscopic
removal has been successful in some cases.
Related Topics