Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 1 : Basic Concepts of Bio Chemistry and Cell Biology
Acids and bases
Acids and bases
An acid
is defined as a substance that gives off protons while a base is a substance
that accepts protons as per the theory of Lowry and Bronsted. Thus, an acid is
a proton (H+) donor and a base is a proton (H+) acceptor.
The
general equation that represents the dissociation of an acid is as follows:

An acid
dissociates to form proton and its conjugate base. On the other hand, the
conjugate base combines with proton to form acid. The difference between an
acid and its conjugate base is the presence or absence of a proton. In general,
a strong acid has a weak conjugate base while a weak acid has a strong
conjugate base. For instance, strong acid HCl has weak conjugate base Cl–,
weak acid HCN has a strong conjugate base CN–
A few examples of acids and their corresponding conjugate bases are as follows.
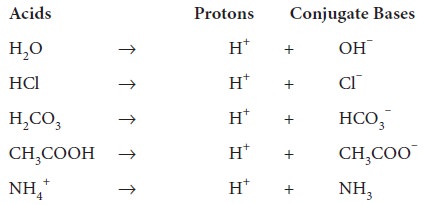
Acids Protons Conjugate Bases
H2O -> H+ + OH–
HCl -> H+ + Cl–
H2CO3 -> H+ + HCO3–
CH3COOH -> H+ + CH3COO‑
NH4+ -> H+ + NH3
Acids and bases in biological systems
In
general, acids are produced in the body as the end products of many metabolic
reactions. These include the volatile acids like carbonic acid (most
predominant, about 20,000 mEq/day) or non-volatile acids (about 80 mEq/day)
such as lactic acid, sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid etc. Carbonic acid is
formed from the metabolic product CO2; lactic acid is produced in
anaerobic metabolism; sulphuric acid is generated from proteins (sulfur
containing amino acids); phosphoric acid is derived from organic phosphates
(e.g. phospholipids). All these acids add up H+ ions to the blood.
The
formation of bases in the body under normal circumstances is negligible. Some
amount of bicarbonate is generated from carbondioxide. The ammonia produced
from amino acids is converted to urea.
Related Topics