Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Attenuation and the trp Operon
trp Multiple Secondary Structures in trp Leader RNA
trp Multiple
Secondary Structures in trp Leader RNA
Once the hairpin secondary structure in the RNA
immediately preceding the trp
attenuation site was associated with transcription termina-tion, several
critical experiments were apparent. One was to examine the consequences of
changing the sequence of the region. Mutations changing the stability of the
hairpin might be expected to alter termination efficiency. A second and easier
experiment was to examine naturally occurring sequence variants. Because
related bacterial strains must have evolved from a common predecessor, they
probably share the same basic mechanism of trp
regulation. If the leader sequences of their trp operons possess structural features in common, these features
are likely to be important in the regulatory mechanisms. Indeed, this was
found. The trp operon in Salmonella typhimurium and Serratiamarcescens also contain leader
regions. Both code for a leader peptidecontaining several tryptophans, and both
mRNAs are capable of form-ing a hairpin just before a string of U’s located
about 20 bases ahead of the trpE
gene.
Close examination of the leader region of the trp operon of E. coli, the trp operons from other strains of
bacteria, and other amino acid biosynthetic operons has revealed two additional
facts. First, the pep-tides encoded by the leader regions always contain one to
seven of the amino acid residues synthesized by that operon. Second, the leader
mRNAs possess at least four regions that can form intramolecular base-paired
hairpins (Fig. 13.11). Here they are numbered 1, 2, 3, and
Figure
13.11 The two possible structures that
the second half of thetrpleaderregion
is capable of assuming. Above is indicated the leader region with the
complementary regions. Opposed arrows at the same height above the leader are
homologous and can base pair. The wavy line below the leader mRNA is the region
encoding the leader peptide.
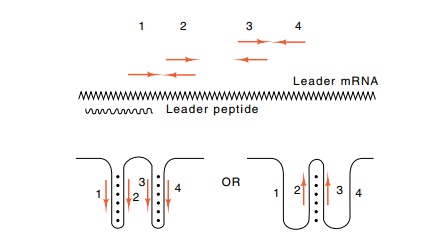
4. The pairing of 3 and 4 forms the hairpin
discussed above that is required for termination of transcription.
Additionally, region 2 can base pair either with region 3 or with region 1.
Likewise, region 3 can base pair with region 2 or 4. The particular hybrids
that form on a leader molecule determine whether transcription of that molecule
will termi-nate as RNA polymerase passes the attenuation region. As we will
see, the pairing choice is regulated by the position on the leader of a
ribosome translating the leader peptide.
Related Topics