Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acid Metabolism
mRNA Processing of tRNA Molecules
mRNA Processing of tRNA Molecules
Most cells have 40 to 50 distinct tRNAs.
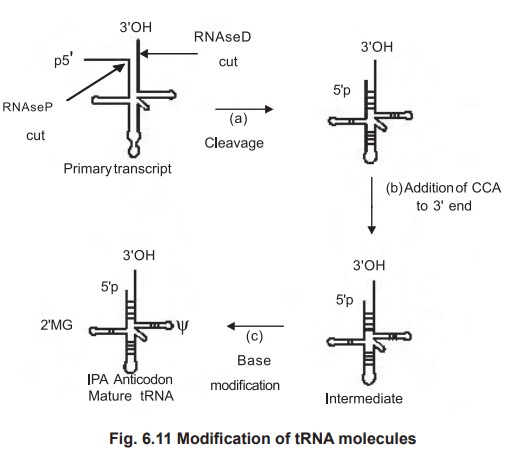
Transfer RNA’s are derived from longer RNA precursors of enzymatic removal of
extranucleotide units from the 5' and 3' ends.
1. Formation of the 3'-OH terminus
This process involves the action of an
endonuclease that recognizes a hairpin loop at the 3' end called RNAse D, which
stops two bases at short of CCA terminus, though it later removes these two
bases after the 5' end is processed. This enzymatic digestion leaves the
molecule called pre-tRNA.
2. Formation of the 5'-P terminus
The 5'-P terminus is formed by an enzyme called
RNAse P, which removes excess RNA from the 5' end of a precursor molecule by an
endonucleolytic cleavage that generates the correct 5' end.
3. Production of modified bases
The final modification is to produce the altered
bases in the tRNA.
In tRNA, two uridines are converted to pseudo
uridine (Ψ), one guanosine to methyl guanosine (MG), one adenine to
isopentyladenine (IPA) etc.
Related Topics