Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acid Metabolism
Sequential Process of Replication Initiation of DNA replication
Sequential Process of Replication Initiation of
DNA replication
o Initiation of DNA synthesis occurs at a site
called origin of replication.
o In prokaryotes, only one origin.
o In eukaryotes, there are multiple origins.
o The origin consists of a short sequence of A = T
base pairs.
Replication bubbles
The two complementary strands of DNA separate at
a site of replication to form a bubble. In eukaryotes many replication bubbles
occur.
Unwinding of parental DNA
After the initiation point is located the
unwinding of the DNA takes place once in every 10 nucleotide pairs. This allows
the “strand separation”.
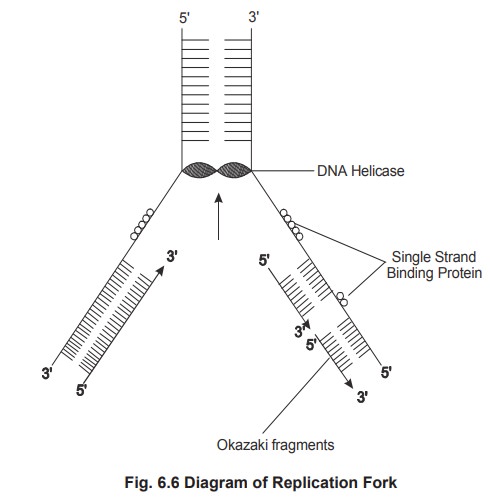
In prokaryotes the unwinding of the structure
occurs with the help of an enzyme called helicase, which requires energy of
hydrolysis of two ATP molecules per base pair broken. Another protein single
strand binding protein (SSB), binds to the unwound DNA to prevent (rewinding)
rejoining.
As the DNA polymerase cannot initiate
replication a primer is a needed and the primer is the small nucleotide of RNA,
synthesised by enzymes primase.
Under the influence of DNA polymerase, in the
presence of Mg2+, the double strands of the DNA acting as a template (or
primer) separate by cleaving the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
The deoxyribo nucleoside triphosphates are attracted from solution in the
cellular sap to form hydrogen bonds with their complementary bases on the
separated strands of the (primer RNA) template dictates the sequence in which
the monomers are assembled.
Polymerisation
During this reaction, each incoming nucleotide
loses a pyrophosphate group and forms an ester linkage with the 3' hydroxyl
group of the deoxyribose on the existing last nucleotide. This linkage is
called “phosphodiester linkage”.
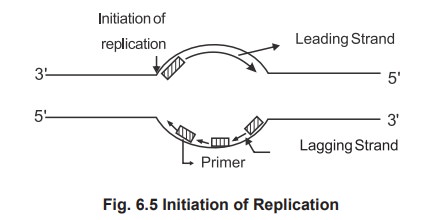
The parental strands run in antiparallel
direction. Synthesis occur simultaneously on both strands, but at different
rates. No enzymes can synthesize 3' ® 5' direction and a single enzyme can not
synthesize both strands. The single enzyme replicates one strand called leading
strand in a continuous manner in 5' to 3' direction (forward), it replicates
the other strand, lagging strand in a discontinuous manner and polymerising
only few (250) nucleotides again run in 5' to 3' at backward direction. This is
called semicontinuous DNA synthesis. The newly synthesized DNA is made as
discontinuous small fragments called as Okazaki fragments and joined by the
enzyme called ligase.
Thus 2 daughter double helices are formed each
consisting of an old strand of the primer DNA and a complementary new strand.
The final composition and nucleotide sequence of each strand is identical with
the corresponding strand in the template (parent) DNA. This process has been
named as replication.
Related Topics