Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acid Metabolism
Catabolism of DNA by Deoxyribonucleases
Catabolism of DNA by Deoxyribonucleases
The nucleic acids exist mainly in the nucleus as
nucleoproteins. These nucleoproteins in the diet are degraded by HCl to nucleic
acids and proteins.
Nucleoproteins----------------(HCL)-----------------> Nucleic acids + proteins
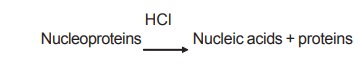
Nucleic acids pass as such from the stomach and
their catabolism starts in duodenum by several enzymes (nucleases,
nucleotidases and nucleosidases) which degrade the nucleic acids to purines,
pyrimidines and pentoses. Three different types of enzymes which degrade the
nucleic acids are discussed one by one.
Nucleases
The enzymes which degrade the nucleic acids are
known as nucleases. Some are specific for RNA and thus known as ribonucleases,
and others for DNA and thus known as dexoyribonucleases, while still some
others are capable of attacking DNA as well as RNA.
Deoxyribonucleases are further classified in to
2 categories.
1. Exonucleases
are the nucleases that
attack only the internucleotide bondslocated at the ends of the nucleic acid.
Exonucleases are further classified into 2
groups.
i.
Those,
which attack the 3' end of single strand DNA called 3' exonuclease
ii.
Those,
which attack the 5' end of the single strand DNA called 5' exonuclease
These 2 enzymes are non specifically called as
phosphodiesterases.
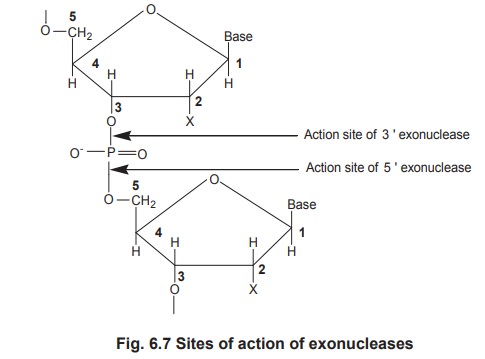
2. Endonucleases
are the nucleases
that attack only the internucleotide bondslocated throughout the length of the
nucleic acid chain (in the middle).
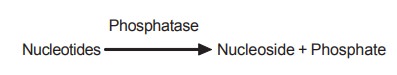
Nucleotidases (Phosphatases)
These enzymes hydrolyse the nucleotides to the
corresponding nucleosides and inorganic phosphate molecules.
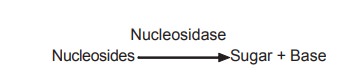
Nucleosidases (Nucleoside phosphorylase)
The nucleosides obtained above either absorbed
or degraded into bases and sugars by nucleosidases.
Related Topics