Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acid Metabolism
Nucleic Acid Metabolism
Nucleic
Acid Metabolism
Introduction
Nucleic acids are the chemical basis of life and
heredity. They serve as transmitters of genetic information. As the name
implies, their location is mainly in nuclei. However, it is also found to be
present in other intracellular organelles. Nucleic acids are present both in
the free state as well as conjucated with proteins (Nucleoproteins). Like amino
acids in proteins, nucleotides are the basic units of nucleic acids. There are
two types of nucleic acids namely,
1.
Ribonucleic
acid
2.
Deoxyribonucleic
acid
Structural Components of Nucleic acids
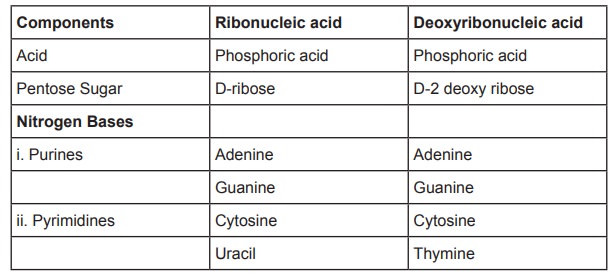
Phosphoric acid
The molecular formula of phosphoric acid is H3PO4.
It contains 3 monovalent hydroxyl groups and a divalent oxygen atom, all linked
to a pentavalent phosphorus atom.
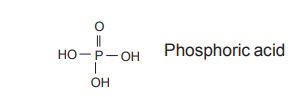
Pentose Sugar
The two types of nucleic acids are distinguished
primarily on the basis of the 5 carbon sugar pentose which they possess. One
possesses D-2-deoxyribose, (deoxyribonucleic acid) while the other contains
D-ribose (hence called ribonucleic acid). Both these sugars in nucleic acids
are present in the furanose form and are of β configuration.
Nitrogenous Bases
Two types of nitrogenous bases are found in all
nucleic acids. These are derivatives of purine and pyrimidine.
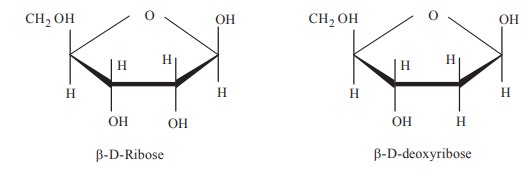
i. Purine Bases
These are all derived from their parent compound
purine, which contains a six membered pyrimidine ring fused to the 5 membered
imidazole ring, the purine derivatives found in nucleic acids are adenine and
guanine.
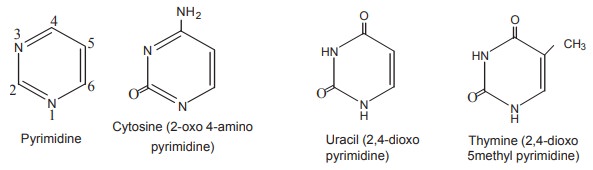
ii. Pyrimidine Bases
These are all derived from their parent
heterocyclic compound pyrimidine. The common pyrimidine derivatives found in
nucleic acids are Uracil, Thymine and Cytosine.
Minor bases in nucleic acid
Apart from the above four bases, certain minor,
unusual bases are also found in DNA and RNA. They are 5 methylcytosine, N4
acetyl cytosine, N6 methyladenine, N6, N6 dimethyladenine and pseudouracil
etc.,
Base Pairing
Base pairing is an essential feature not only to
maintain the double helical structure of DNA, but also plays an important role
in DNA, RNA and protein biosynthesis.
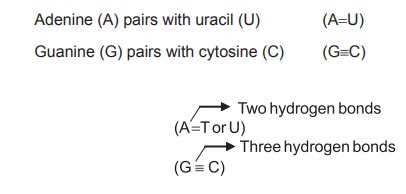
In DNA
Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) (A=T)
Guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C) (G≡C)
In RNA
Adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U) (A=U)
Guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C) (G≡C)
Chargaffs rule of DNA composition
DNA has equal number of adenine and thymine
residues (A=T) and equal number of guanine and cytosine (G≡C) residues. This is
known as Chargaffs rule of molar equivalence between purine and pyrimidines in
DNA.
Structure of Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the fundamental units of nucleic
acids. Each nucleotide is comprising of a
i)
Phosphate
group ii) Pentose Sugar and iii) Nitrogenous base.
Sugar + Base ------------>
Nucleoside
Nucleoside + Phosphate ----------->Nucleotide
Related Topics