Example, Merits, Limitations, Example Illustration, Solution | Methods of providing depreciation | Accountancy - Written down value / Diminishing balance method | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 10 : Depreciation Accounting
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 10 : Depreciation Accounting
Written down value / Diminishing balance method
Written down value / Diminishing
balance method
Under this method, depreciation
is charged at a fixed percentage on the written down value of the asset every
year. Hence, it is called written down value method. Written down value is the
book value of the asset, i.e., original cost of the asset minus depreciation
upto the previous accounting period. As the amount of depreciation goes on
decreasing year after year, it is called diminishing balance method or reducing
installment method.
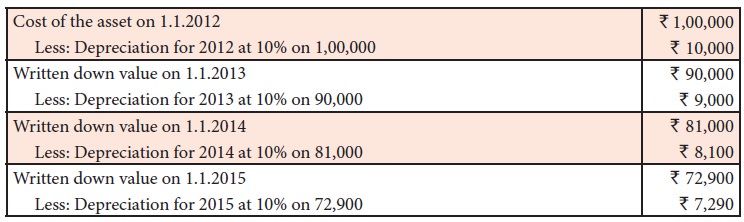
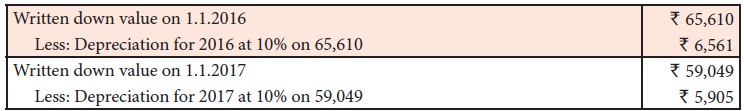
Example
On 1.1.2012, a firm purchased a
machine at a cost of Rs. 1,00,000. Depreciation charged at 10% p.a. on
written down value method for the five years is as follows:
Merits
Following are the merits of
written down value method.
(a) Equal charge against income
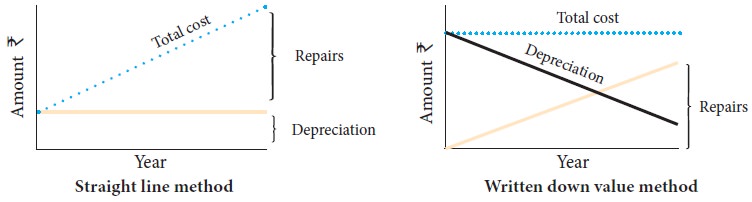
In the initial years depreciation is high and repair charges are low. When the asset becomes older, the amount of depreciation charged is less but repair charges are high. Hence, the total burden on profit in respect of depreciation and repairs put together remains almost similar year after year.
(b) Logical method
In the earlier years, when the asset is more productive, high
depreciation is charged. In the later years when the asset becomes less
productive, the depreciation charge is less.
Limitations
Following are the limitations of written down value method.
(a) Assets cannot be completely written off
Under this method, the value of an asset even if it becomes obsolete and
useless, cannot be reduced to zero and some balance would continue in the asset
account.
(b) Ignores the interest factor
This method does not take into account the loss of interest on the
amount invested in the asset. The amount would have earned interest, had it
been invested outside the business is not considered.
(c) Difficulty in determining the rate of depreciation
Under this method, the rate of providing depreciation cannot be easily
determined. The rate is generally kept higher because it takes very long time
to write off an asset down to its scrap value.
(d) Ignores the actual use of the asset
Under this method, a fixed rate of depreciation is provided on the
written down value of the asset by applying the predetermined rate of
depreciation on its original cost. But, the actual use of the asset is not
considered in the computation of depreciation.
Suitability
This method is suitable in case of assets having a comparatively long
life and which require considerable repairs in the later years when they become
older. Examples are building and plant and machinery.
Illustration
A firm purchased a plant on
1.1.2018 for Rs. 9,000 and
spent Rs. 1,000 as
erection charges. Calculate the amount of depreciation for the year 2018 @ 15%
per annum under the written down value method. Accounts are closed on 31st
March every year.
Solution
Original cost = 9,000 +
1,000 = 10,000
Rate of depreciation = 15%
Date of purchase = 1.1.2018
Number of months used = 1.1.2018 to 31.03.2018 = 3 months
Amount of depreciation = 15% on 10,000 for 3 months
= 10,000 ×15% × 3/12 = Rs. 375
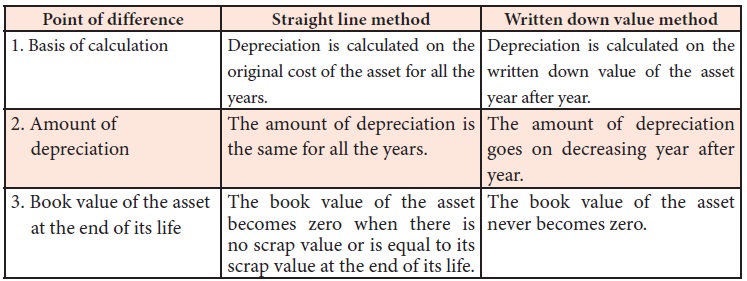
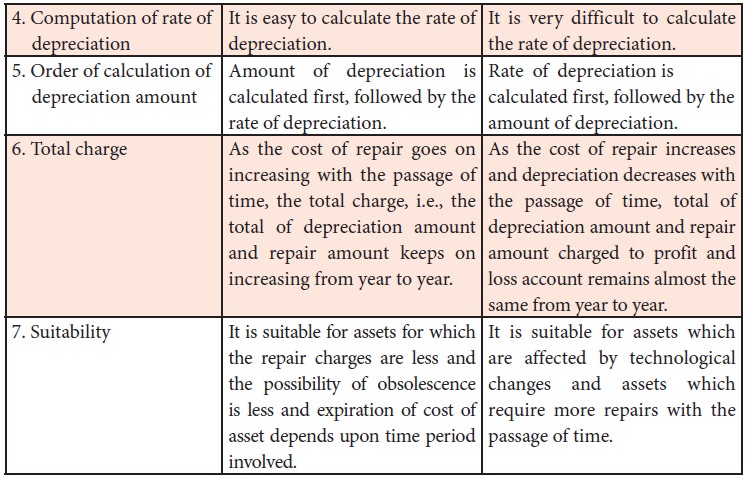
Differences between straight line method and written down value method
Following are the differences
between straight line method and written down value method
Related Topics