Example, Merits, Limitations, Example Illustration, Solution | Methods of providing depreciation | Accountancy - Straight line method/ Fixed instalment method / Original cost method | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 10 : Depreciation Accounting
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 10 : Depreciation Accounting
Straight line method/ Fixed instalment method / Original cost method
Straight
line method/ Fixed instalment method / Original cost method
Under this method, a fixed percentage on the original cost of the asset
is charged every year by way of depreciation. Hence it is called original cost
method. As the amount of depreciation remains equal in all years over the
useful life of an asset it is also called as fixed instalment method. When the
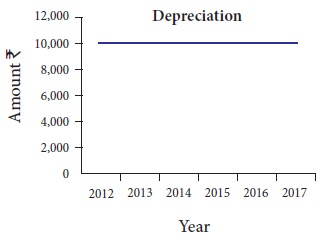
amount of depreciation charged over its life is plotted on a graph and the
points are joined together, the graph will show a horizontal straight line.
Hence, it is called straight line method.
This method is suitable for those assets the useful life of which can be
estimated accurately and which do not require much expense on repairs and
renewals.
Under this method, the following
formulae are used for calculating the amount of depreciation and the rate of
depreciation respectively:

Tutorial note
·
In the year of purchase, if the period of use is
less than a year, the amount of depreciation will be charged proportionately
for the period for which the asset has been used in the business.
·
If depreciation is deducted from the cost of the
asset at the end of useful life of the asset the amount left in the asset
account will be equal to the scrap value if there is any scrap value or it will
be zero if there is no scrap value.
Example
On 1.1.2012, a firm purchased a
machine at a cost of Rs. 1,10,000. Its life was estimated to be 10
years with a scrap value of Rs. 10,000. The amount of depreciation to be
charged at the end of each year is:

When it is plotted on a graph for
5 years, it appears as follows:
Merits
Following are the merits of
straight line method of depreciation:
(a) Simple and easy to understand
Computation of depreciation under
this method is very simple and is easy to understand.
(b) Equality of depreciation burden
Under this method, equal amount of depreciation is debited to the profit and loss account each year. Hence, the burden of depreciation on the profit of each year is equal..
(c) Assets can be completely written off
Under this method, the book value of an asset can be reduced to zero if
there is no scrap value or to the scrap value at the end of its useful life.
Thus the asset account can be completely written off.
(d) Suitable for the assets having fixed working life
This method is appropriate for the fixed assets having certain fixed
period of working life. In such cases, the estimation of useful life is easy and
in turn it helps in easy determination of rate of depreciation.
Limitations
Following are the limitations of
straight line method of depreciation:
(a) Ignores the actual use of the asset
Under this method, a fixed amount of depreciation is provided on each
asset by applying the predetermined rate of depreciation on its original cost.
But, the actual use of the asset is not considered in computation of
depreciation.
(b) Ignores the interest factor
This method does not take into account the loss of interest on the
amount invested in the asset. That is, the amount would have earned interest,
had it been invested outside the business is not considered.
(c) Total charge on the assets will be more when the asset becomes older
With the passage of time, the cost of maintenance of an asset goes up.
Hence, the amount of depreciation and cost of maintenance put together is less
in the initial period and goes up year after year. But, this method does not
consider this.
(d) Difficulty in the determination of scrap value
It may be quite difficult to assess the true scrap value of the asset
after a long period say 10 or 15 years after the date of its installation.
Suitability
Straight line method of depreciation is suitable in case of fixed assets
in respect of which useful life can be determined and maintenance and repair
cost is the same throughout the life of the asset.
Illustration 1
On 1.1.2017 a firm purchased a machine at a cost of Rs. 1,00,000. Its life was estimated to be 10
years with a scrap value of Rs. 10,000.
Compute the amount of depreciation to be charged at the end of each year.
Solution
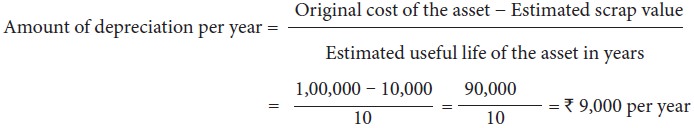
Illustration 2
A company has purchased a
machinery for Rs. 1,80,000 and
spent Rs. 10,000 for
its installation. The estimated life of the machinery is 5 years with a
residual value of Rs. 15,000. Find
out the amount of depreciation to be provided every year.
Solution

Illustration 3
From the following information, calculate the amount of depreciation and
rate of depreciation under straight line method.
Purchase price of machine Rs.
2,00,000
Expenses to be capitalised Rs.
50,000
Estimated residual value Rs.
15,000
Expected useful life 5
years
Solution
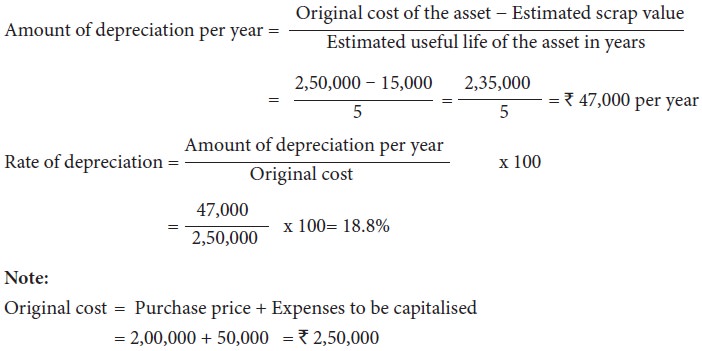
Illustration 4
Find out the rate of depreciation under straight line method from the
following details:
Original cost of the asset = Rs. 10,000
Estimated life of the asset = 10 years
Estimated scrap value at the end = Rs. 2,000
Solution

Related Topics