Chapter: User Interface Design : Windows and controls
Window Presentation Styles
Window
Presentation Styles
The presentation style of a window refers to its
spatial relationship to other windows.
There are two basic styles, commonly called tiled
or overlapping.
Tiled
Windows
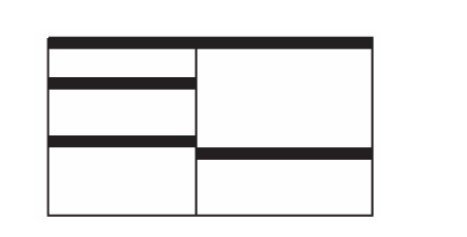
Tiled windows derive their name from common floor
or wall tile. Tiled windows appear in one plane on the screen and expand or
contract to fill up the display surface, as needed.
Most systems provide two-dimensional tiled windows,
adjustable in both height and width.
advantages:
The system usually allocates and positions windows
for the user, eliminating the necessity to make positioning decisions.
Open windows are always visible, eliminating the
possibility of them being lost and forgotten.
Every window is always completely visible,
eliminating the possibility of information being hidden.
They are perceived as fewer complexes than
overlapping windows, possibly because there are fewer management operations or
they seem less “magical.”
They are easier, according to studies, for novice
or inexperienced people to learn and use.
They yield better user performance for tasks where
the data requires little window manipulation to complete the task.
Disadvantages
Only a limited number can be displayed in the
screen area available.
As windows are opened or closed, existing windows
change in size. This can be annoying.
As windows change in size or position, the movement
can be disconcerting.
As the number of displayed windows increases, each
window can get very tiny.
The changes in sizes and locations made by the
system are difficult to predict.
The configuration of windows provided by the system
may not meet the user’s needs.
They are perceived as crowded and more visually
complex because window borders are flush against one another, and they fill up
the whole screen. Crowding is accentuated if borders contain scroll bars or
control icons. Viewer attention may be drawn to the border, not the data.
They permit less user control because the system
actively manages the windows.
Overlapping
Windows
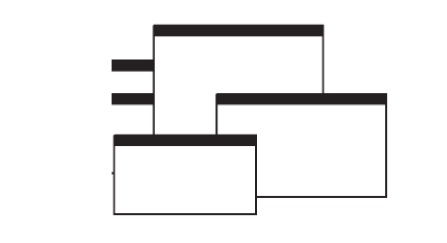
Overlapping windows may be placed on top of one another like papers on a
desk.
They possess a three-dimensional quality, appearing to lie on different
planes.
Advantages:
Visually, their look is three-dimensional,
resembling the desktop that is familiar to the user.
Greater control allows the user to organize the
windows to meet his or her needs.
Windows can maintain larger sizes.
Windows can maintain consistent sizes.
Windows can maintain consistent positions.
Screen space conservation is not a problem, because
windows can be placed on top of one another.
There is less pressure to close or delete windows
no longer needed.
The possibility exists for less visual crowding and
complexity. Larger borders can be maintained around window information, and the
window is more clearly set off against its background. Windows can also be
expanded to fill the entire display.
They yield better user performance for tasks where
the data requires much window manipulation to complete the task.
Disadvantages
They are operationally much more complex than tiled
windows. More control functions require greater user attention and
manipulation.
Information in windows can be obscured behind other
windows.
Windows themselves can be lost behind other windows
and be presumed not to exist.
That overlapping windows represent a
three-dimensional space is not always realized by the user.
Control freedom increases the possibility for
greater visual complexity and crowding. Too many windows, or improper
offsetting, can be visually overwhelming.
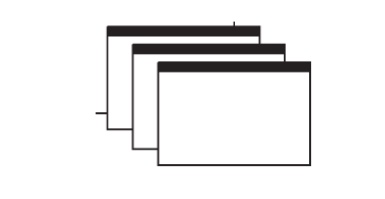
Cascading
Windows
A special type of overlapping window has the windows automatically
arranged in a regular progression.
Each window is slightly offset from others, as illustrated in Figure
Advantages
No window is ever completely hidden.
Bringing any window to the front is easier.
It provides simplicity in visual presentation and
cleanness.
Picking a
Presentation Style
Use tiled windows for:
·
Single-task activities.
·
Data that needs to be seen simultaneously.
·
Tasks requiring little window manipulation.
·
Novice or inexperienced users.
Use overlapping windows for:
·
Switching between tasks.
·
Tasks necessitating a greater amount of window
manipulation.
o Expert or
experienced users.
·
Unpredictable display contents.
Related Topics