Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : EMR and Its Interaction With Atmosphere and Earth Material
Wavelength Regions Important To Remote Sensing
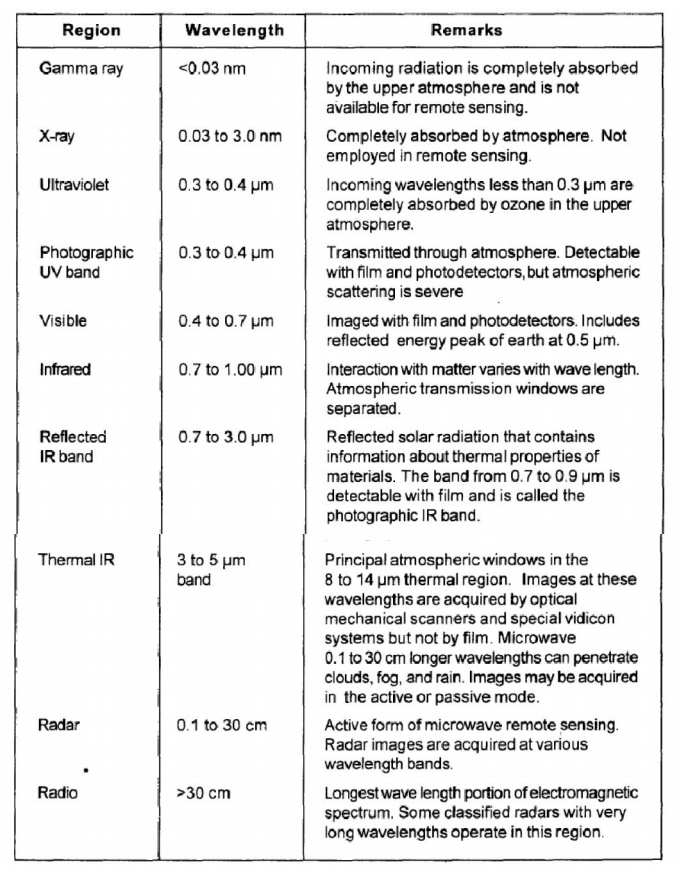
WAVELENGTH REGIONS IMPORTANT TO REMOTE SENSING:
1 Ultraviolet or UV
For the most purposes ultraviolet
or UV of the spectrum shortest wavelengths are practical for remote sensing.
This wavelength beyond the violet portion of the visible wavelengths hence it
name. Some earth surface materials primarly rocks and materials are emit
visible radiation when illuminated by UV radiation.
2 Visible Spectrum
The light which our eyes - our
"remote sensors" - can detect is part of the visible spectrum.
It is important to recognize how small the visible portion is relative to the
rest of the spectrum. There is a lot of radiation around us which
is"invisible" to our eyes, but can be
detected by other remote sensing
instruments and used to our advantage. The visible wavelengths
cover a range from approximately 0.4 to 0.7 ?m. The longest visible wavelength
is red and the shortest is
violet. Common wavelengths of what we perceive as particular colours from the
visible portion of the spectrum are listed below. It isimportant to note that
this is the only portion of the spectrum we can associate with the concept of colours.
Violet: 0.4 -0.446
?m
Blue: 0.446 -0.500
?m
Green: 0.500 -0.578
?m
Yellow: 0.578 -0.592
?m
Orange: 0.592 -0.620
?m
Red: 0.620 -0.7
?m
Blue,
green, and red are the primary colours or wavelengths of the
visible spectrum. Theyare defined as such because no single primary
colour can be created from the other two, but all other colours can be formed
by combining blue, green, and red in various proportions. Although we see
sunlight as a uniform or homogeneous colour, it is actually composed of various
wavelengths of radiation in primarily the ultraviolet, visible and infrared
portions of the spectrum. The visible portion of this radiation can be shown in
its component colours when sunlight is passed through a prism, which
bends the light in differing amounts according to wavelength.
3 Infrared (IR)
The next portion of the spectrum
of interest is the infrared (IR) region which covers the wavelength range from
approximately 0.7 ?m to 100 ?m more than 100 times as wide
as the
visible portion. The
infrared can be
divided into 3
categories based on
their radiation
properties-the reflected near- IR middle IR and thermal IR.
The
reflected near IR covers wavelengths from approximately 0.7 ?m to 1.3 ?m is
commonly used to expose black and white and color-infrared
sensitive film.
The
middle-infrared
region includes energy with a wavelength of 1.3 to 3.0 ?m.
The
thermal IR region is quite different than the visible and reflected IR
portions, as
this energy is essentially the
radiation that is emitted from the Earth's surface in the form of heat.
The thermal IR covers wavelengths from approximately 3.0 ?m to 100 ?m.
Microwave
This wavelength (or frequency)
interval in the electromagnetic spectrum is commonly referred to as a band,
channel or region.The major subdivision
The
portion of the spectrum of more recent interest to remote sensing is the
microwave region from about 1 mm to 1 m. This covers the longest wavelengths
used for remote sensing. The shorter wavelengths have properties similar to the
thermal infrared region while the longer wavelengths approach the wavelengths
used for radio broadcasts.
Related Topics