Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : EMR and Its Interaction With Atmosphere and Earth Material
Remote Sensing And Its Components
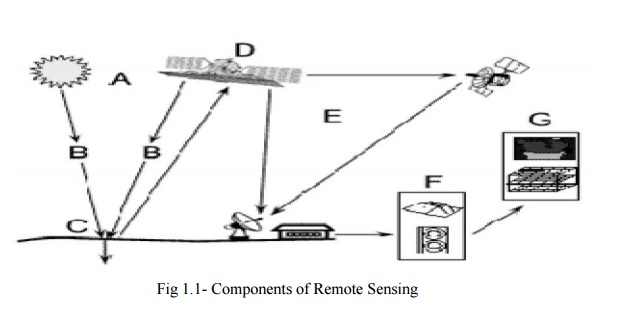
REMOTE SENSING AND ITS COMPONENTS:
Remote sensing is the science of
acquiring information about the Earth's surface without actually bein g in
contact with it. This is done by sen sing and recording reflected or emitted
energy and processing, analyzing, and applying th at information." In
much of
remote sensing, the process
involves an interaction betee n incident adiation and the targets of
interest. T his is exemplified by the use of imaging systems where the
following seven elements are involved. However that remote sensg also involves
the sensing of emitted energy and the use of non-imaging sensors.
1. Energy Source or Illumination (A) - the first
requirement for remote sensing is to
have an energy source which illuminates or provides
electromagnetic energy to the target of interest.
2. Radiation
and the Atmosphre (B) - as the energy travels from
its source to the target, it will
come in contact with and interact with the atmosphere it passes
through. This interaction may take place a second time as the energy travels
from the target to the sensor.
3. Interaction with the Target (C) - once the
energy makes its way to the target through the atmosphere, it interacts with
the target depending on the properties of both the target and the radiation.
4. Recording of Energy by the Sensor (D) - after
the energy has been scattered by, or emitted from the target, we require a
sensor (remote - not in contact with the target) to collect and record the
electromagnetic radiation.
5. Transmission, Reception, and Processing (E) -
the energy recorded by the sensor has to be transmitted, often in electronic
form, to a receiving and processing station where the data are processed into
an image (hardcopy and/or digital).
6. Interpretation and Analysis (F) - the processed
image is interpreted, visually and/or digitally or electronically, to extract
information about the target which was illuminated.
7. Application (G) - the final element of the
remote sensing process is achieved when we apply the information we have been
able to extract from the imagery about the target in order to better understand
it, reveal some new information, or assist in solving a particular problem.
HISTRY OF REMOTE SENSING:
1839 -
first photograph
![]()
1858 -
first photo from a balloon
![]()
1903 -
first plane
![]()
![]() 1909 first photo from a plane 1903-4 -B/W
infrared film
1909 first photo from a plane 1903-4 -B/W
infrared film
![]()
WW I and WW II 1960 - space
![]()
![]()
Related Topics