Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : EMR and Its Interaction With Atmosphere and Earth Material
Atmospheric Windows
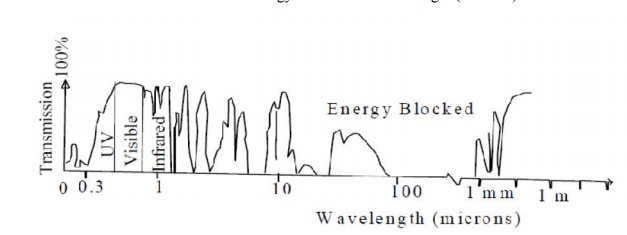
ATMOSPHERIC WINDOWS
While EMR is transmitted from the
sun to the surface of the earth, it passes through the atmosphere. Here,
electromagnetic radiation is scattered and absorbed by gases and dust
particles. Besides the major atmospheric gaseous components like molecular nitrogen
and oxygen, other constituents like water vapour, methane, hydrogen, helium and
nitrogen compounds play important role in modifying electro magnetic radiation.
This affects image quality. Regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in which
the atmosphere is transparent are called atmospheric windows. In other words,
certain spectral regions of the electromagnetic radiation pass through the
atmosphere without much attenuation are called atmospheric windows. The
atmosphere is practically transparent in the visible region of the
electromagnetic spectrum and therefore, many of the satellite based remote
sensing sensors are designed to collect data in this region. Some of the
commonly used atmospheric windows are shown in the figure.
Figure . They are: 0.38-0.72
microns (visible), 0.72-3.00 microns (near infra-red and middle infra-red), and
8.00-14.00 microns (thermal infra-red).
Transmission100%UVVisibleInfraredEnergy Blocked0.3 Wavelength (microns)1101001 mm
Related Topics