Physics Practical Experiment - Voltage-Current Characteristics of a Zener Diode | 12th Physics : Practical
Chapter: 12th Physics : Practical
Voltage-Current Characteristics of a Zener Diode
VOLTAGE-CURRENT CHARACTERISTICS OF
A ZENER DIODE
AIM
To
draw the voltage-current (V-I) characteristic curves of a Zener diode and to
determine its knee voltage, forward resistance and reverse breakdown voltage.
APPARATUS REQUIRED
Zener
diode IZ5.6V, variable dc power supply (0 ŌĆō 15V), milli ammeter, volt meter,
470ŌĆå╬® resistance, and connecting wires.
FORMULA
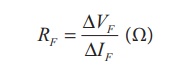
where,
RF
ŌåÆ Forward resistance of the diode (╬®)
ŌłåVF
ŌåÆ The change in forward voltage (volt)
ŌłåIF
ŌåÆ The change in forward current (mA)
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
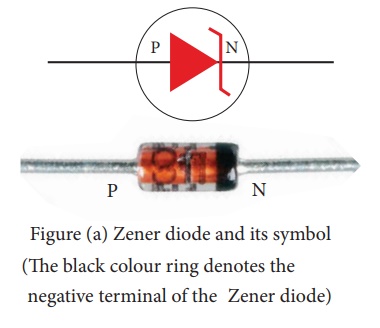
Figure (a) Zener diode and its symbol (The black colour ring denotes the negative terminal of the Zener diode)
Figure
(b) Zener diode in forward bias
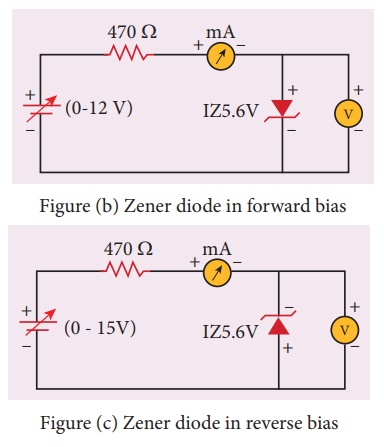
Figure
(c) Zener diode in reverse bias
Precaution
Care
should be taken to connect the terminals of ammeter, voltmeter, dc power supply
and the Zener diode with right polarity.
PROCEDURE
i) Forward bias characteristics
┬Ę
In the forward bias, the P- region of
the diode is connected to the positive terminal and N-re-gion to the negative
terminal of the DC power supply.
┬Ę
The connections are given as per the
circuit diagram.
┬Ę
The voltage across the diode can be
varied with the help of the variable DC power supply.
┬Ę
The forward voltage (VF)
across the diode is increased from 0.1V in steps of 0.1V up to 0.8V and the
forward current (IF) through the diode is noted from the
milli-ammeter. The read-ings are tabulated.
┬Ę
The forward voltage and the forward
current are taken as positive.
┬Ę
A graph is drawn taking the forward voltage
along the x-axis and the forward current along the y-axis.
┬Ę
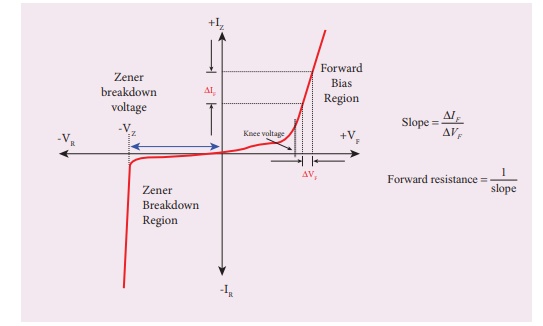
The voltage corresponding to the dotted
line in the forward characteristics gives the knee voltage or threshold voltage
or turn-on voltage of the diode.
┬Ę
The slope in the linear portion of the
forward characteristics is calculated. The reciprocal of the slope gives the
forward resistance of the diode.
ii) Reverse bias characteristics
┬Ę
In the reverse bias, the polarity of the
DC power supply is reversed so that the P- region of the diode is connected to
the negative terminal and N-region to the positive terminal of the DC power
supply
┬Ę
The connections are made as given in the
circuit diagram.
┬Ę
The voltage across the diode can be
varied with the help of the variable DC power supply.
┬Ę
The reverse voltage (VR)
across the diode is increased from 0.5V in steps of 0.5V up to 6V and the
reverse current (IR) through the diode is noted from the
milli-ammeter. The readings are tabulated.
┬Ę
Initially, the voltage is increased in
steps of 0.5V. When the breakdown region is approxi-mately reached, then the
input voltage may be raised in steps of, say 0.1V to find the break-down
voltage.
┬Ę
The reverse voltage and reverse current
are taken as negative.
┬Ę
A graph is drawn taking the reverse bias
voltage along negative x-axis and the reverse bias current along negative
y-axis.
┬Ę
In the reverse bias, Zener breakdown
occurs at a particular voltage called Zener voltage VZ (~5.6 to
5.8V) and a large amount of current flows through the diode which is the
character-istics of a Zener diode.
┬Ę
The breakdown voltage of the Zener diode
is determined from the graph as shown.
OBSERVATION
Table 1 Forward bias characteristic curve
Table 2 Reverse bias characteristic
curve
CALCULATION
(i)
Forward resistance RF =
(ii)
knee voltage =
(iii)
The breakdown voltage of the Zener diode VZ = ----V
RESULT
The
V-I characteristics of the Zener diode are studied.
(i)
Forward resistance RF =
(ii)
knee voltage =
(iii)
The breakdown voltage of the Zener diode VZ= ----V
Practical Tips
┬Ę
The DC power supply voltage should to be
increased only up to the specified range in the forward (0 ŌĆō 2ŌĆåV) and reverse
(0 ŌĆō 15ŌĆåV) directions.
┬Ę
The voltage applied beyond this limit
may damage the resistor or the diode.
┬Ę
Zener diode functions like an ordinary
PN junction diode in the forward direction. Hence the forward characteristic is
the same for both PN junction diode and Zener diode. Therefore, knee voltage
and forward resistance can be determined as explained in the previous experiment.
┬Ę
Unlike ordinary PN junction diode, the
reverse current in Zener diode is measured using milli-ammeter due to the large
flow of current.
Related Topics