Physics Practical Experiment - Refractive Index of the Material of the Prism | 12th Physics : Practical
Chapter: 12th Physics : Practical
Refractive Index of the Material of the Prism
REFRACTIVE INDEX OF THE MATERIAL OF
THE PRISM
AIM
To
determine the refractive index of the material of a prism using spectrometer.
APPARATUS REQUIRED
Spectrometer,
prism, prism clamp, sodium vapour lamp, spirit level.
FORMULA
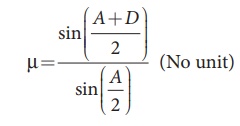
where,
ÎĽ
→ Refractive index of the material of the prism (No unit)
A
→ Angle of the prism (degree)
D
→ Angle of minimum deviation (degree)
DIAGRAMS
PROCEDURE
1) Initial adjustments of the spectrometer
·
Eye-piece: The eye-piece of the
telescope is adjusted so that the cross-wires are seen clearly.
·
Slit: The slit of the collimator is
adjusted such that it is very thin and vertical.
·
Base of the spectrometer: The base of
the spectrometer is adjusted to be horizontal using leveling screws.
·
Telescope: The telescope is turned
towards a distant object and is adjusted till the clear inverted image of the
distant object is seen. Now the telescope is adjusted to receive parallel rays.
·
Collimator: The telescope is brought in
line with the collimator. Collimator is adjusted until a clear image of the
slit is seen in the telescope. Now the collimator gives parallel rays.
·
Prism table: Using a spirit level, the
prism table is adjusted to be horizontal with the three leveling screws
provided in the prism table.
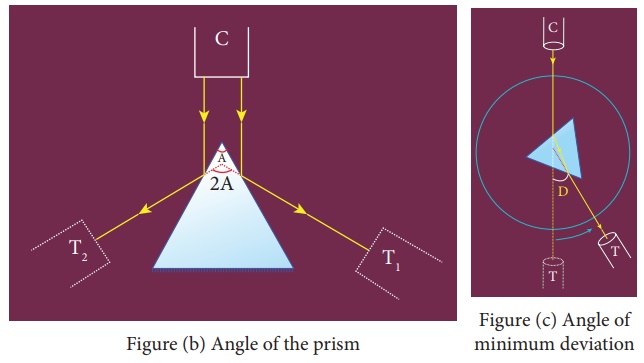
2) Determination of angle of the prism (A)
·
The slit is illuminated by yellow light
from sodium vapour lamp.
·
The given equilateral prism is placed on
the prism table in such a way that refracting edge of the prism is facing the
collimator.
·
The light emerging from the collimator
is incident on both reflecting faces of the prism and is reflected.
·
The telescope is rotated towards left to
obtain reflected image of the slit from face 1 of the prism and is fixed.
·
Using tangential screws, the telescope
is adjusted until the vertical cross-wire coincides with the reflected image of
the slit.
·
The main scale reading and vernier
coincidence are noted from both vernier scales.
·
The telescope is now rotated towards
right to obtain the reflected image from face 2 of the prism. As before, the
readings are taken.
·
The difference between the two readings
gives 2A from which the angle of the prism A is calculated.
3) Determination of angle of minimum deviation (D)
·
The prism table is rotated such that the
light emerging from the collimator is incident on one of the refracting faces
of the prism, gets refracted and emerges out from the other refracting face.
·
The telescope is turned to view the
refracted image.
·
Looking through the telescope, the prism
table is rotated in such a direction that the image moves towards the direct
ray.
·
At one particular position, the
refracted ray begins to retrace its path. The position where the refracted
image returns is the position of minimum deviation.
·
The telescope is fixed in this position
and is adjusted until the vertical cross-wire coincides with the refracted
image of the slit.
·
The readings are taken from both vernier
scales.
·
The prism is now removed and the
telescope is rotated to obtain the direct ray image and the readings are taken.
·
The readings are tabulated and the
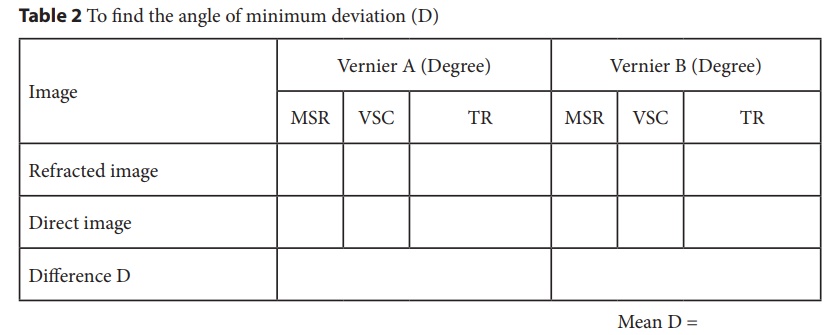
difference between these two readings gives the angle of minimum deviation D.
·
From the values of A and D, the
refractive index of the material of the glass prism is deter-mined.
Least count
1
MSD = 30′
Number
of vernier scale divisions = 30
For
spectrometer, 30 vernier scale divisions will cover 29 main scale divisions.
30
VSD = 29 MSD
Or
1
VSD = 29 / 30 MSD
Least
count (LC) = 1 MSD – 1 VSD
=
1 / 30 MSD
=
1′
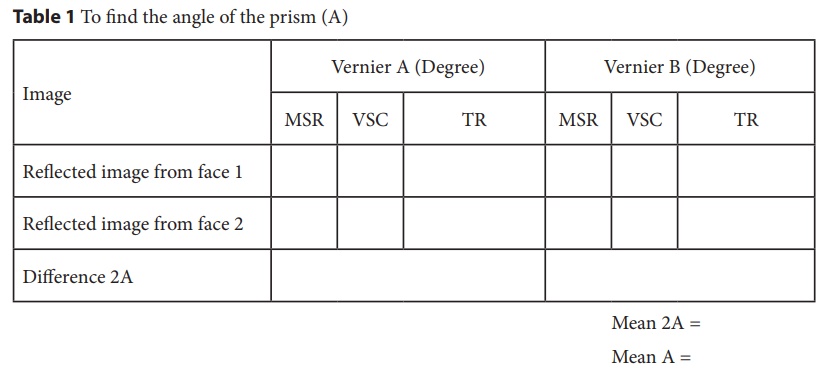
OBSERVATION
Table
1 To find the angle of the prism (A)
Table
2 To find the angle of minimum deviation (D)
RESULT
1.
Angle of the Prism (A) = ............ (degree)
2.
Angle of the minimum deviation of the prism (D) =............. (degree)
3.
Refractive index of the material of the Prism (ÎĽ) =............. (No unit)
Note:
i)
Once initial adjustments are done, spectrometer should not be disturbed.
ii)
Total reading TR = MSR + (VSC Ă— LC)
Where
MSR
→ Main Scale Reading
VSC
→ Vernier Scale Coincidence
LC
→ Least count (= 1′)
Related Topics