Chapter: Electric Energy Generation and Utilisation and Conservation : Wind Energy
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines(VAWT): Schematic Structure, Advantage, Disadvantages
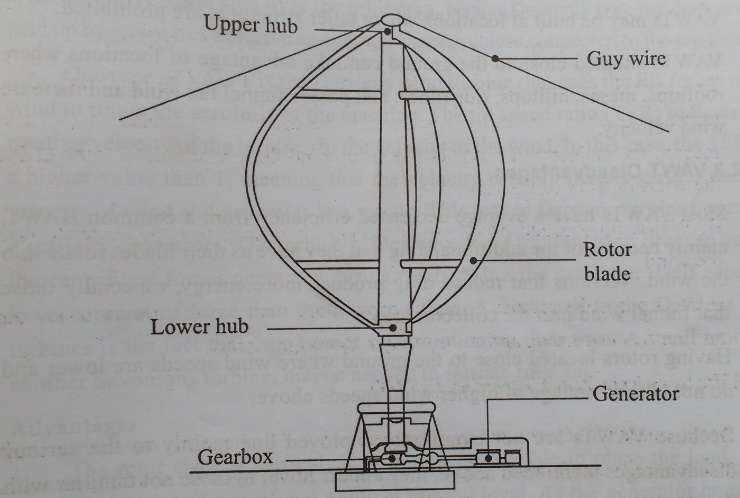
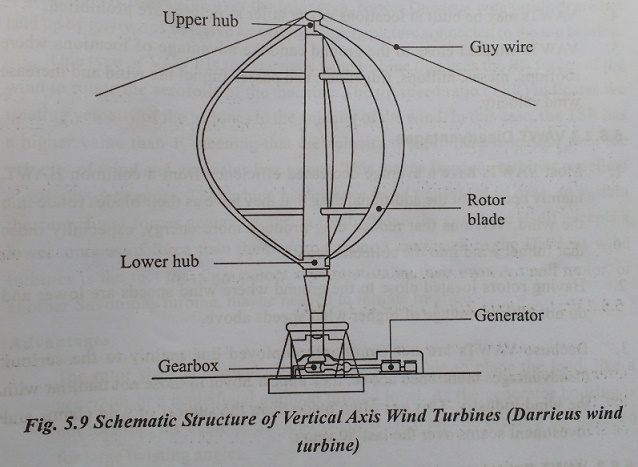
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines(VAWT)
Vertical wind turbines, as shortened to VAWTs, have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically as shown in Fig 5.9. The main advantage of this arrangement is that the wind turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind. This is an advantage on site where the wind direction is highly variable or has turbulent winds.
With a vertical axis, the generator and other primary components can be placed near the ground, so the tower does not need to support it, also makes maintenance easier. The main drawback of a VAWT generally create drag when rotating into the wind.
It is difficult to mount vertical-axis turbines on towers, meaning they are often installed nearer to the base on which they rest, such as the ground or a building rooftop. The wind speed is slower at a lower altitude, so less wind energy is available for a given size turbine. Air flow near the ground and other objects can create turbulent flow, which can introduce issues of vibration, including noise and bearing wear which may increase the maintenance or shorten its service life. However, when a turbine is mounted on a rooftop, the building generally redirects wind over the roof and this can double the wind speed at the turbine. If the height of the rooftop mounted turbine tower is approximately 50% of the building height, this is near the optimum for maximum wind energy and minimum wind turbulence.
Important points to remember recording VAWT:
Nacelle is placed at the bottom.
Drag is the main force
Yaw mechanism is not required
Lower starting torque
Difficulty in mounting the turbine
Unwanted fluctuations in the power output
VAWT Advantages
1. No yaw mechanisms is needed
2. A VAWT can be located nearer the ground, making it easier to maintain the moving parts.
3. VAWTs have lower wind startup speeds than the typical the HAWTs.
4. VAWTs may be built at locations where taller structures are prohibited.
5. VAWTs situated close to the ground can take advantage of locations where rooftops, means hilltops, ridgelines, and passes funnel the wind and increase wind velocity.
VAWT Disadvantage
1. Most VAWTs have a average decreased efficiency from a common HAWT, mainly because o the additional drag that they have as their blades rotate into the wind. Versions that reduce drag produce more energy, especially those that funnel wind into the collector area.
2. Having rotors located close to the ground where wind speeds are lower and do not take advantage of higher wind speeds above.
3. Because VAWTs are not commonly deployed due mainly to the serious disadvantage mentioned above, they appear novel to those not familiar with the wind industry. This has often made them the subject of wild claims and investment scams over the last 50 years.
Related Topics