Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : Pharmacology of nitric oxide (NO)
Vascular effects of nitric oxide
Vascular effects of nitric
oxide
The pharmacological activity
of nitric oxide was recog-nized before it was identified as a physiological
mediator it-self. This discovery was made during an investigation into the
nature of the so-called `endothelium-derived relaxing factor' (EDRF). The
activity of EDRF can be triggered by the application of acetylcholine to the
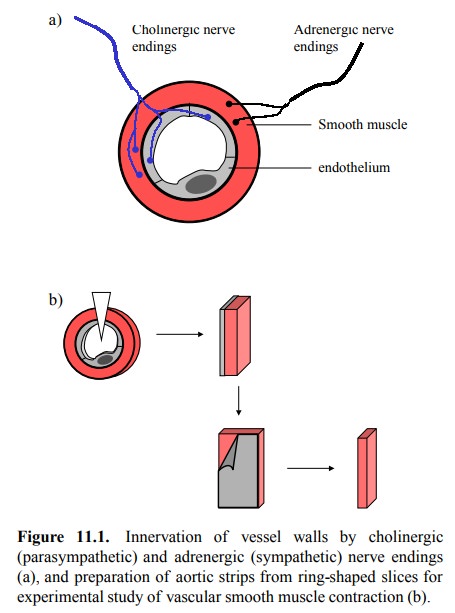
aorta of experimen-tal animals. In the aorta (as well as other blood vessels),
not only the smooth muscle itself but also the endothelium is supplied with
cholinergic nerve terminals and accord-ingly possesses acetylcholine receptors,
which are of the muscarinic type (Figure 11.1a). After cutting the aorta into
strips (Figure 11.1b), the endothelium can be removed me-chanically or
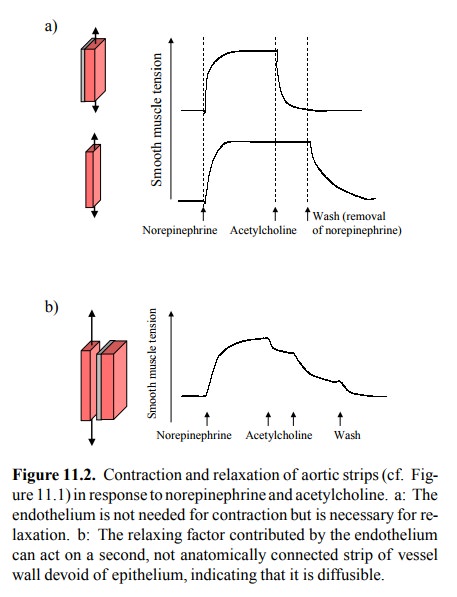
enzymatically1. Aortic strips with or without endothelium will both
respond with contraction to nora-drenaline or α-selective adrenergic agonists. However, if
acetylcholine is applied subsequently, only the strip that re-tains its
endothelium will respond with relaxation, whereas the one without will stay
contracted. Thus, the endothelium is required for the relaxation of the smooth
muscle to occur (Figure 11.2a). If a strip with the endothelium removed is
placed next to one retaining the endothelium, and the entire assembly is
exposed to first norepinephrine and then acetyl-choline, the endothelium-less
strip will still relax, indicat-ing that EDRF is a diffusible substance (Figure
11.2b).
Approximately
at the same time that EDRF was identi-fied as NO, it was found that the common
mode of action of several drugs containing nitrate or similar functional groups
consisted in the release of nitric oxide. The identi-ty of EDRF and NO was
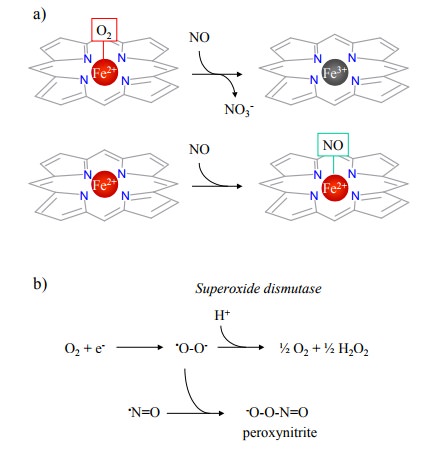
initially suspected based on cir-cumstantial evidence: Both NO and EDRF were
found to bind to and be inactivated by hemoglobin (Figure 11.3a). Furthermore,
the effects of both were augmented by super-oxide dismutase. This enzyme
scavenges superoxide an-ions by disproportionation into O2 and H2O2.
Since super-oxide reacts very rapidly with NO, superoxide dismutase will
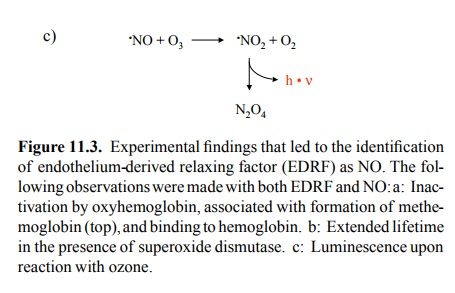
increase the lifetime and biological effect of NO (Fig-ure 11.3b). The identity
was finally established by the direct detection of NO in biological samples
using a chemilumi-nescence assay (Figure 11.3c).
Related Topics