Chapter: Biochemical Pharmacology : Pharmacology of nitric oxide (NO)
Nitric oxide synthase and its isoforms
Nitric oxide synthase and its
isoforms
NO is
generated in vivo by nitric oxide synthase (NOS). This enzyme is located in the
cytosol and utilizes argi-nine, molecular oxygen, and NADPH as substrates
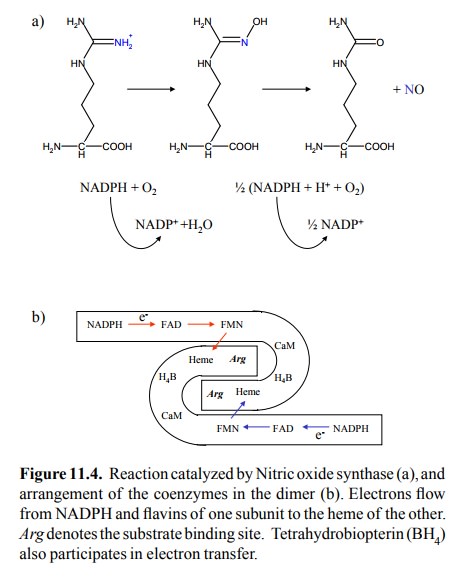
(Figure 11.4a). NOS is a fairly complex molecule that possesses multiple redox
coenzymes which constitute a little electron transport chain of their own. NOS
is a dimer, and the elec-tron transfer actually occurs between the two subunits
(Fig-ure 11.4b). There are several subtypes of NOS: Endothelial NOS or eNOS,
neuronal NOS or nNOS, and inducible NOS or iNOS. eNOS is responsible for the
blood vessel-relaxing effect discussed above. Of note, it is found in both
arter-ies and veins. Accordingly, its activation will both lower resistance (by
arterial relaxation) and increase volume ca-pacity (by venous relaxation), and
therefore cause a strong reduction of blood pressure. In fact, NO-releasing
drugs are the most powerful vasodilatators available, overriding the action of
other mediators such as norepinephrine (see above). They also have a very
prompt onset of action, and they are used when lowering of blood pressure or
release of vasospasms must be achieved immediately.
Neuronal
NOS is found in the central nervous system, where NO fulfils the role of yet
another neurotransmitter. NO signalling between neurons works in much the same
way as between endothelial and smooth muscle cells, i.e. it does not involve a
receptor on the cell surface (see be-low). iNOS is found in macrophages, which
are one of the major types of phagocytic cells. NO released within and from
macrophages serves an entirely different purpose – that of an antimicrobial
effector mechanism (see later). The two different roles of NO – mediator in
blood vessels and the central nervous system (CNS), microbicide in the
macrophage – are reflected by different control mecha-nisms of the
corresponding NOS isoforms. Whereas eNOS and nNOS are controlled by Ca++
/ calmodulin (providing for very rapid and dynamic control), iNOS is controlled
by transcriptional activation (which is much slower but also much longer
sustained).
Related Topics