Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Using AWT Controls, Layout Managers, and Menus
Using Lists - AWT Controls
Using Lists
The List class provides
a compact, multiple-choice, scrolling selection list. Unlike the Choice object, which shows only the
single selected item in the menu, a List
object can be constructed to
show any number of choices in the visible window. It can also be created to
allow multiple selections. List
provides these constructors:
List( ) throws HeadlessException
List(int numRows) throws
HeadlessException
List(int numRows, boolean
multipleSelect) throws
HeadlessException
The first version creates a List
control that allows only one item to be selected at any one time. In the second
form, the value of numRows specifies
the number of entries in the list that will always be visible (others can be
scrolled into view as needed). In the third form, if multipleSelect is true, then the user may select two or
more items at a time. If it is false, then only one item may be selected.
To add a selection to the list, call add( ). It has the following two forms:
void add(String name)
void add(String name, int
index)
Here, name is the name of
the item added to the list. The first form adds items to the end of the list.
The second form adds the item at the index specified by index. Indexing begins at zero. You can specify –1 to add the item
to the end of the list.
For lists that allow only single selection, you can determine which
item is currently selected by calling either getSelectedItem( ) or getSelectedIndex(
). These methods are shown here:
String getSelectedItem( ) int getSelectedIndex( )
The getSelectedItem( )
method returns a string containing the name of the item. If more than one item
is selected, or if no selection has yet been made, null is returned. getSelectedIndex(
) returns the index of the item. The first item is at index 0. If more than
one item is selected, or if no selection has yet been made, –1 is returned.
For lists that allow multiple selection, you must use either getSelectedItems( ) or getSelectedIndexes( ), shown here, to
determine the current selections:
String[ ] getSelectedItems( ) int[ ] getSelectedIndexes( )
getSelectedItems( ) returns an array containing
the names of the currently selected items.
getSelectedIndexes( ) returns an
array containing the indexes of the currently selected items.
To obtain the number of items in the list, call getItemCount( ). You can set the
currently selected item by using the select(
) method with a zero-based integer index. These methods are shown here:
int getItemCount( ) void select(int index)
Given an index, you can obtain the name associated with the item at
that index by calling getItem( ),
which has this general form:
String getItem(int index)
Here, index specifies the
index of the desired item.
Handling Lists
To process list events, you will need to implement the ActionListener interface. Each time a List item is double-clicked, an ActionEvent object is generated. Its getActionCommand( ) method can be used
to retrieve the name of the newly selected item. Also, each time an item is
selected or deselected with a single click, an ItemEvent object is generated. Its getStateChange( ) method can be used to determine whether a
selection or deselection triggered
this event. getItemSelectable( )
returns a reference to the object that triggered this event.
Here is an example that converts the Choice controls in the preceding section into List components, one multiple choice and the other single choice:
//
Demonstrate Lists.
import
java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.applet.*; /*
<applet
code="ListDemo" width=300 height=180> </applet>
*/
public
class ListDemo extends Applet implements ActionListener { List os, browser;
String
msg = "";
public
void init() {
os = new
List(4, true); browser = new List(4, false);
// add
items to os list
os.add("Windows");
os.add("Android");
os.add("Solaris");
os.add("Mac OS");
// add
items to browser list
browser.add("Internet
Explorer"); browser.add("Firefox"); browser.add("Chrome");
browser.select(1);
//add lists to window
add(os);
add(browser);
//register to receive action events
os.addActionListener(this);
browser.addActionListener(this);
}
public
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) { repaint();
}
//
Display current selections.
public
void paint(Graphics g) {
int
idx[];
msg =
"Current OS: ";
idx =
os.getSelectedIndexes(); for(int i=0; i<idx.length; i++)
msg +=
os.getItem(idx[i]) + " "; g.drawString(msg, 6, 120);
msg =
"Current Browser: ";
msg +=
browser.getSelectedItem(); g.drawString(msg, 6, 140);
}
}
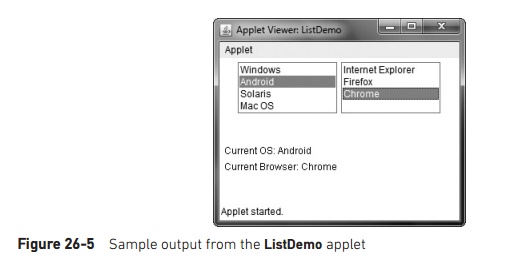
Sample output generated by the ListDemo
applet is shown in Figure 26-5.
Related Topics