Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Using AWT Controls, Layout Managers, and Menus
Choice Controls - AWT Controls
Choice Controls
The Choice class is used
to create a pop-up list of items from
which the user may choose. Thus, a Choice
control is a form of menu. When inactive, a Choice component takes up only enough space to show the currently
selected item. When the user clicks on it, the whole list of choices pops up,
and a new selection can be made. Each item in the list is a string that appears
as a left-justified label in the order it is added to the Choice object. Choice defines
only the default constructor, which creates an empty list.
To add a selection to the list, call add( ). It has this general form: void add(String name)
Here, name is the name of
the item being added. Items are added to the list in the order in which calls
to add( ) occur.
To determine which item is currently selected, you may call either getSelectedItem( ) or getSelectedIndex( ). These methods are
shown here:
String getSelectedItem( )
int getSelectedIndex( )
The getSelectedItem( )
method returns a string containing the name of the item. getSelectedIndex( ) returns the index of the item. The first item
is at index 0. By default, the first
item added to the list is selected.
To obtain the number of items in the list, call getItemCount( ). You can set the
currently selected item using the select(
) method with either a zero-based integer index or a string that will match
a name in the list. These methods are shown here:
int getItemCount( ) void select(int index) void select(String name)
Given an index, you can obtain the name associated with the item at
that index by calling getItem( ),
which has this general form:
String getItem(int index)
Here, index specifies the
index of the desired item.
Handling Choice Lists
Each time a choice is selected, an item event is generated. This is
sent to any listeners that previously registered an interest in receiving item
event notifications from that component. Each listener implements the ItemListener interface. That interface
defines the itemStateChanged( )
method. An ItemEvent object is
supplied as the argument to this method.
Here is an example that creates two Choice menus. One selects the operating system. The other selects
the browser.
//
Demonstrate Choice lists.
import
java.awt.*;
import
java.awt.event.*;
import
java.applet.*; /*
<applet
code="ChoiceDemo" width=300 height=180> </applet>
*/
public
class ChoiceDemo extends Applet implements ItemListener { Choice os, browser;
String
msg = "";
public
void init() { os = new Choice();
browser
= new Choice();
//add items to os list
os.add("Windows");
os.add("Android"); os.add("Solaris"); os.add("Mac
OS");
//add items to browser list
browser.add("Internet Explorer");
browser.add("Firefox"); browser.add("Chrome");
//add choice lists to window
add(os);
add(browser);
//register to receive item events
os.addItemListener(this);
browser.addItemListener(this);
}
public
void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent ie) { repaint();
}
//
Display current selections.
public
void paint(Graphics g) {
msg =
"Current OS: ";
msg +=
os.getSelectedItem(); g.drawString(msg, 6, 120); msg = "Current Browser:
";
msg +=
browser.getSelectedItem(); g.drawString(msg, 6, 140);
}
Sample output is shown in Figure 26-4.
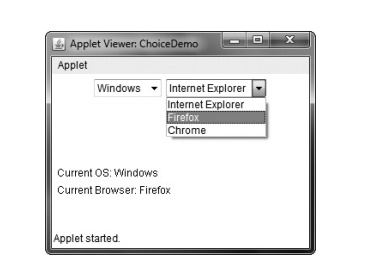
Figure 26-4 Sample output from the ChoiceDemo applet
Related Topics