Chapter: Object Oriented Analysis and Design
UML Class diagrams
UML Class diagrams
Class
diagrams are widely used to describe the types of objects in a system and their
relationships. Class diagrams model class structure and contents using design
elements such as classes, packages and objects.
Class
diagrams describe three different perspectives when designing a system,
conceptual, specification, and implementation. These perspectives become
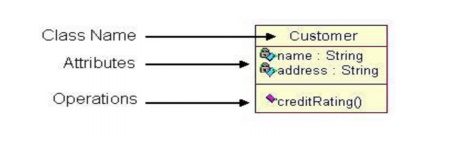
evident as the diagram is created and help solidify the design.Classes are
composed of three things: a name, attributes, and operations. Below is an
example of a class.
Class
diagrams also display relationships such as containment, inheritance,
associations and others. Below is an example of an associative relationship:
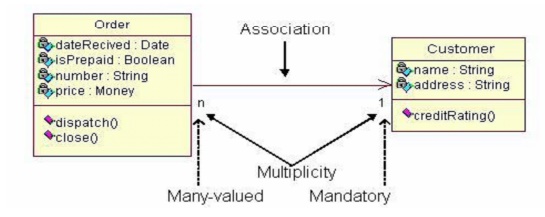
The
association relationship is the most common relationship in a class diagram.
The association shows the relationship between instances of classes.
For
example, the class Order is associated with the class Customer. The
multiplicity of the association denotes the number of objects that can
participate in the relationship. For example, an Order object can be associated
to only one customer, but a customer can be associated to many orders. Another
common relationship in class diagrams is a generalization.
A
generalization is used when two classes are similar, but have some differences.
Look at the generalization below:
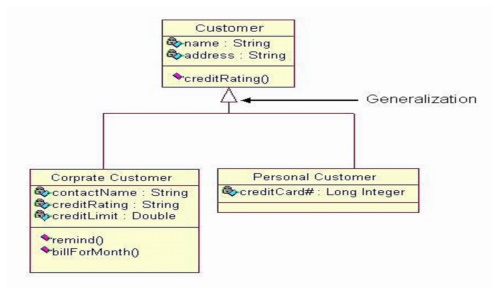
In
this example the classes Corporate Customer and Personal Customer have some
similarities such as name and address, but each class has some of its own
attributes and operations.
The
class Customer is a general form of both the Corporate Customer and Personal
Customer classes. This allows the designers to just use the Customer class for
modules and do not require in-depth representation of each type of customer.
When
to Use: Class Diagrams
Class
diagrams are used in nearly all Object Oriented software designs. Use them to
describe the Classes of the system and their relationships to each other.
How
to Draw: Class Diagrams
Class
diagrams are some of the most difficult UML diagrams to draw. To draw detailed
and useful diagrams a person would have to study UML and Object Oriented
principles for a long time.
Therefore,
this page will give a very high level overview of the process. To find list of
where to find more information see the Resources page. Before drawing a class
diagram consider the three different perspectives of the system the diagram
will present; conceptual, specification, and implementation. Try not to focus
on one perspective and try see how they all work together.
When
designing classes consider what attributes and operations it will have. Then
try to determine how instances of the classes will interact with each other.
These are the very first steps of many in developing a class diagram. However,
using just these basic techniques one can develop a complete view of the software
system.
Related Topics