Chapter: Physics : Properties of Mater and Thermal Physics
Types of Stress and Strain
INTRODUCTION
Elasticity is a branch of physics
which deals with the elastic property of materials. When an external force is
applied to a body, there will be some change in its length, shape and volume. When
this external force is removed, and if the body regains its original shape and
size, then the body is said to be a Perfectly Elastic body. If the body
does not regain its original shape and size after removal of the applied force,
then it is said to be Perfectly Plastic body.
STRESS
AND STRAIN
A body is said to be rigid
body, if the distance between any two points in a body is unaltered due to
application of the force. In practice no body is perfectly rigid. When a body
is subjected to some external forces the body will offer some resistance to the
deforming forces, as a result some work is done on the body and this work is
stored as the elastic potential energy. Now if the deforming forces re removed
the energy stored brings back the body to its original condition.
STRESS
Stress is define as the
restoring force per unit area which brings back the body to its original value
from the deformed state. As long as no permanent change is produced in the body,
the restoring force is equal to the force applied. Unit of stress is N/m2.
TYPES
OF STRESS
1.
Normal
stress
When the force is applied along the surface of the body, then the stress
applied is Normal Stress.
2.
Tangential
Stress
When the force is applied along the
surface of the body, then the stress applied is called as tangential stress.
The tangential stress is also called as Shearing Stress.
STRAIN
Strain
is defined as the change in dimension (fractional deformation) produced by the
external force of the body. In other way it can also defined as the ration of
the change in dimension to the original dimension.
Strain=Change in.
Dimension \ Original. Dimension
TYPES
OF STRAIN
a. Longitudinal or
tensile strain
Definition:
it is defined as ratio between the changes in length to the original length
without any change in its shape, after the removal of the external forces.
Explanation:
When
a force is applied along it length of the body of the original length ‘L ‘, due
to this applied force if the change in length is l then
Longitudinal Strain=l\L
b. Shearing Strain
Definition:
It is defined as the angular deformation produced on the body due to the
application of external tangential forces on it.
Explanation
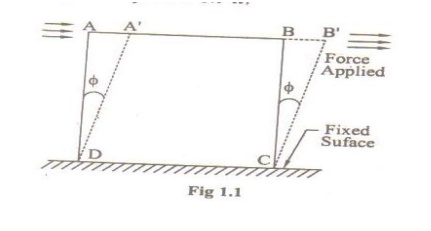
Let ABCD
be a body with its CD fixed a shown in the figure. A tangential force is
applied on the upper surface AB of the body. Therefore the body shears to angle
ø and it goes to a position A’B’CD. Then this angle ø
measured in radians is called shearing strain.
c. Volumetric Strain
Definition:
it is defined as the ration betweenthe change in volume to the original volume
without any change in its shape.
Explanation: When
forces are applied normal to the surface of the body of volume ‘V’, it
undergoes a change in volume (V), then
Volumetric Strain=v\V
Related Topics