Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 1 : Applications of Matrices and Determinants
Transition Probability Matrices
Transition Probability Matrices
Forecasting the succeeding state when the initial market share is given
One stage Transition Probability
The Occurrence of an event at a specified point in time, put the system in state Sn; if after the passage of one unit of time, another event occurs, that is the system moved from the state Sn to Sn+1. This movement is related to a probability distribution, there is a probability associated with each (move) transition from event Sn to Sn+1. This probability distribution is called one stage transition probability.
Transition Matrix
The transition Probabilities Pjk satisfy Pjk > 0, ŌłæPjk = 1 for all j
These probabilities may be written in the matrix form

This is called the transition probability matrix
Example 1.25
Consider the matrix of transition probabilities of a product available in the market in two brands A and B.
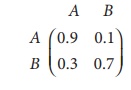
Determine the market share of each brand in equilibrium position.
Solution:
Transition probability matrix

Hence the market share of brand A is 75% and the market share of brand B is 25%
Example 1.26
Parithi is either sad (S) or happy (H) each day. If he is happy in one day, he is sad on the next day by four times out of five. If he is sad on one day, he is happy on the next day by two times out of three. Over a long run, what are the chances that Parithi is happy on any given day?
Solution:
The transition porbability matrix is
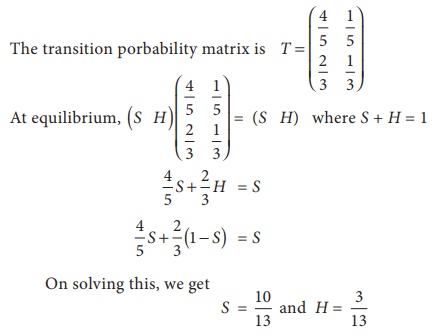
In the long run, on a randomly selected day, his chances of being happy is 10/13 .
Example 1.27
Akash bats according to the following traits. If he makes a hit (S), there is a 25% chance that he will make a hit his next time at bat. If he fails to hit (F), there is a 35% chance that he will make a hit his next time at bat. Find the transition probability matrix for the data and determine AkashŌĆÖs long- range batting average.
Solution:
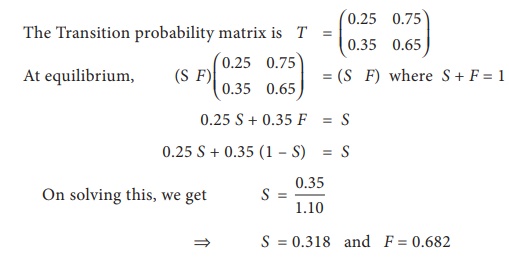
Ōł┤ AkashŌĆÖs batting average is 31.8%
Example 1.28
80% of students who do maths work during one study period, will do the maths work at the next study period. 30% of students who do english work during one study period, will do the english work at the next study period.
Initially there were 60 students do maths work and 40 students do english work. Calculate,
(i) The transition probability matrix
(ii) The number of students who do maths work, english work for the next subsequent 2 study periods.
Solution
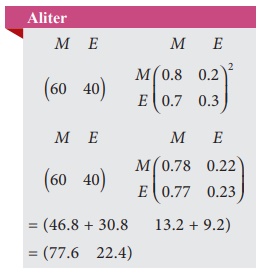
(i) Transition probability matrix
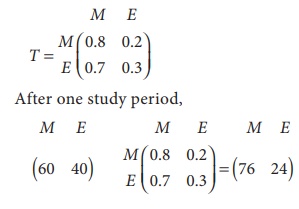
So in the very next study period, there will be 76 students do maths work and 24 students do the English work.
After two study periods,
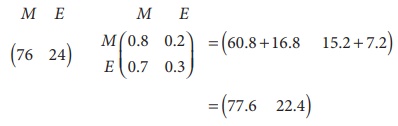
After two study periods there will be 78 (approx) students do maths work and 22 (approx) students do English work.
Related Topics