Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: Body Composition
Total body potassium - Indirect methods in Body composition techniques
Total body potassium
Chemical carcass analysis has revealed that the amount of potassium in the fat-free body is relatively con-stant, although the amount of potassium in different tissues varies widely. The determination of total body potassium (TBK) is relatively easy, owing to the natural occurrence of three potassium isotopes (39K, 40K, and 41K), in constant relative amounts, of which 40K is radioactive (gamma emission). Counting the emission of the gamma rays from the body reveals the amount of radioactive potassium, from which TBK and hence FFM can be calculated. The chamber in which the subject is scanned has to be carefully shielded to avoid any background radiation (cosmic radiation). The scanning of the body for potassium lasts for 20–30 min and the reproducibility is 2–3%.
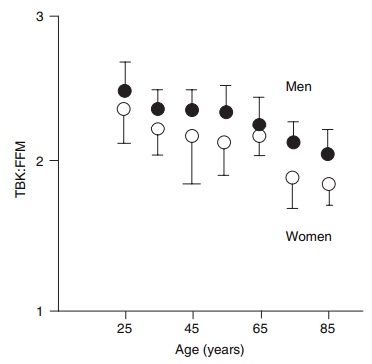
Several authors have shown that the amount of potassium in the FFM is different between males and females, is lower in obese subjects, and is probably also age dependent. Thus, TBK is much more useful as a measure of body cell mass (BCM) than as a measure of FFM. However, this discrepancy can be used to calculate the “quality” of FFM, defined as the ratio of cellular to extracellular components of FFM, or operationally as BCM/FFM. Thus, when TBK is used to assess BCM, and another method such as hydrodensitometry or DXA is used to assess FFM independently, it can be shown that the quality of FFM declines with age, along with the quantity (Figure 2.2). When potassium values are used to calculate intracellular water, BCM, or FFM, assuming constant amounts of potassium in these body components, the same errors can occur as with densitometry and dilu-tion techniques.
Although the technique is easy to apply in patients, the high cost of the scanning instrumentation limits its use other than in research settings.
Related Topics