Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: Body Composition
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry - Indirect methods in Body composition techniques
Dual-energy
X-ray absorptiometry
During DXA (also known as DEXA), the body or part of the body is scanned with X-rays of two distinct levels of energy. The attenuation of the tissues for the two different levels of radiation depends on its chemi-cal composition and is detected by photocells.
The instrument’s software generates a
two-dimensional picture of the body or the body compartment under study. The
software can calculate several body com-ponents: bone mineral content and bone
mineral density, lean mass, and adipose tissue fat mass. These calculations are
possible for each of the body parts, e.g., for legs, trunk, spine, femur, and
arms. However, the method cannot distinguish between subcutane-ous adipose
tissue and discrete adipose tissue sites such as perirenal adipose tissue. The
reproducibility of DXA is very high, varying from about 0.5% for bone mineral
density to about 2% for total body com-position. The reproducibility for
regional body com-position is less. The method is quick and easy to perform and
places very few demands on the subject. The radiation dose (0.02 mSv) is only a
fraction of the radiation dose of a normal chest radiograph, and hardly higher
than the normal background. Apart from repeated scanning, the radiation dose
should not be a limiting factor in terms of volunteers being exposed to
hazardous levels of radiation. A disadvan-tage of the method is that the
attenuation of the X-rays depends on the thickness of the tissue. Therefore,
correction for the body size has to be made. Compared with traditional methods,
DXA scanning is easy and widely available which, in turn, leads to prediction equations
for body composition based on DXA. However, as with other methods, DXA relies
on certain assumptions and there are many publications showing that the error
in body composi-tion measurements using DXA can be considerable (Figure 2.3).
Moreover, identical machines, even using the same software versions, can give
different results in scanning the same person.
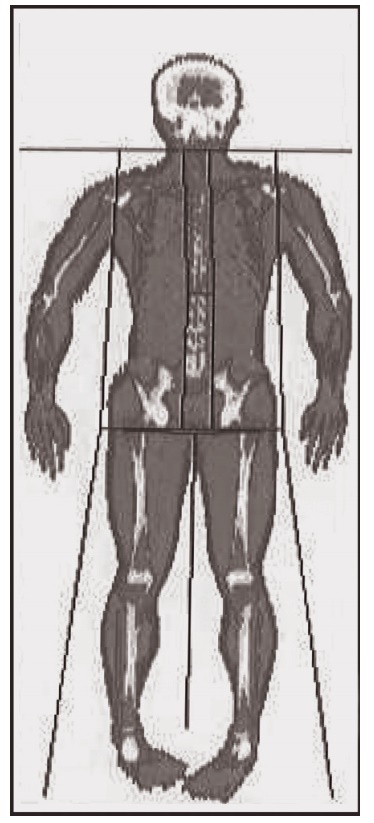
Figure 2.3 Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometer (DXA) scan using a HOLOGIC whole-body DXA (QDR-4500). Subcutaneous body fat, bone, and muscle are distinguished by different colors.
Related Topics