Chapter: Essential Microbiology: Microorganisms in the Environment
The carbon cycle - Microorganisms in the Environment
The carbon
cycle
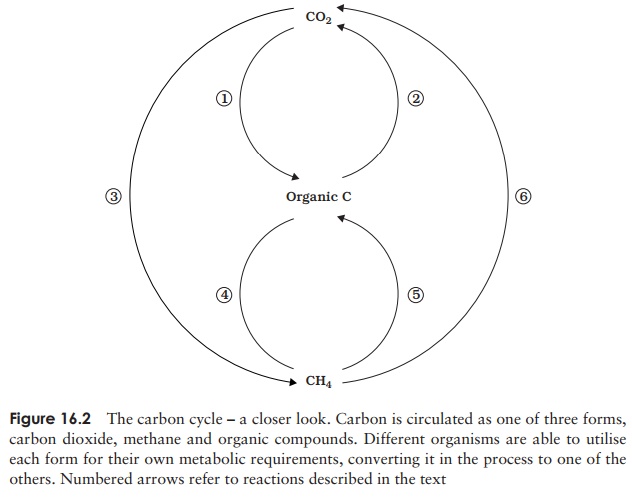
A more detailed scheme of the carbon cycle is shown in Figure
16.2. Both aerobic and anaerobic reactions con-tribute to the cycle. The
numbers in parentheses in the following description refer to those in Figure
16.2.
Atmospheric CO2 is fixed into organic compounds by
plants, together with phototrophic and chemoau-totrophic microorganisms (1). The organic compounds thus
synthesised undergo cellular respiration and CO2 is returned to the
atmosphere (2). The carbon may have
been passed along a food chain to consumers before this occurs. Carbon dioxide
is also produced by the decomposition of dead plant, animal and microbial
material by heterotrophic bacteria and fungi.
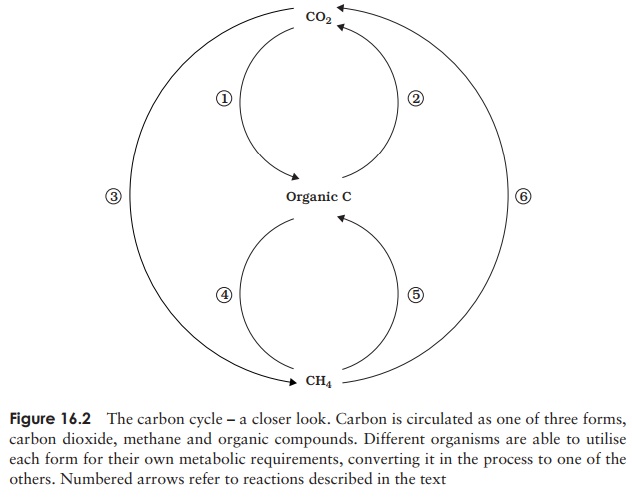
Methanogenic bacteria produce methane from organic carbon or CO2
(3, 4). This in turn is oxidised by methanotrophic bacteria; carbon may
be incorporated into organic material or lost as CO2 (5, 6).
Related Topics