Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering Thermodynamics : The Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second law of Thermodynamics
The Second law of Thermodynamics
Kelvin Planck’s:
It is impossible statement to constructa device that,
operating continuously, will produce no effect other than
transfer of heat from a single thermal reservoir and performance of an equal
amount of work.
The term thermal
reservoir refers to a very large system in stable equilibrium, to which or from
which, any amount of heat can be transferred at constant temperature.
A thermal reservoir
supplying heat continuously at constant temperature is known as source.
(Example : Sun)
A thermal reservoir
receiving heat continuously at constant temperature is known as sink. (Examples
: River, Sea)
From
Kelvin-Planck statement it is clear that for any system to operate in a cycle
and to give out work continuously it should interact with a minimum of two
reservoirs at different temperatures. The system will receive heat from the
high temperature reservoir and reject heat to the low temperature reservoir.
Such devices are known as heat engines. Performance (or) Efficiency of a heat
engine can be expressed as the ratio of desired output to the required input. In
a heat engine the desired output is net work output and the required input is
total heat input
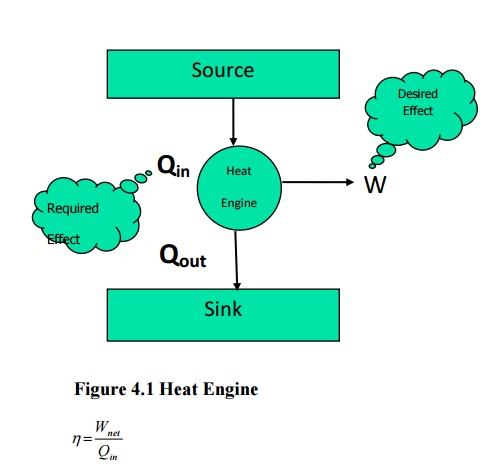
From
first law of thermodynamics
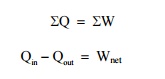
Clausius statement : Unaided
by an external agency heat can not be transferred from a body at lower
temperature
to a body at higher temperature.
Devices
that are used to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature to a body at
higher temperature are known as refrigerators (or) heat pumps. If the high
temperature side is atmosphere it is a refrigerator. If the low temperature
side is atmosphere it is known as a heat pump. The performance index here is
called coefficient of performance (COP). In refrigerator (and heat pumps) the
performance is the ratio of two independent parameters and hence the
possibility of getting the value more than unity is always there. But the term
efficiency is restricted to a maximum of unity. Hence the term efficiency is
not used here.

COP=Q/W
Taking
work as external agency, for refrigerators (Figure 4.2)
From
first law
QS= SW
Q1
-Q2 =W
COP
= Q2
/ Q1 – Q2
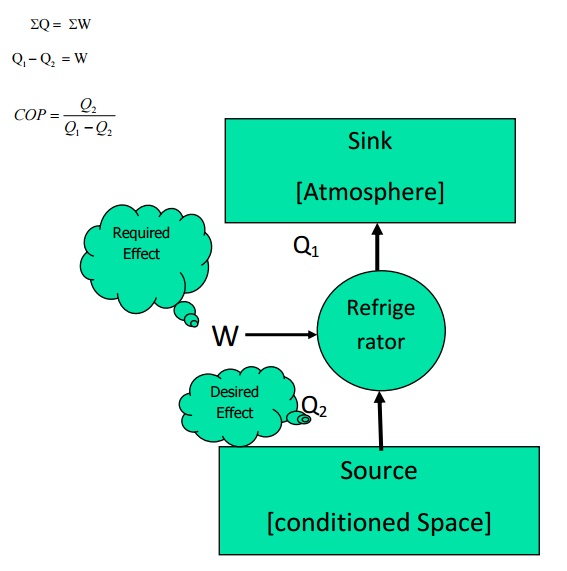
Figure
4.2 Refrigerator

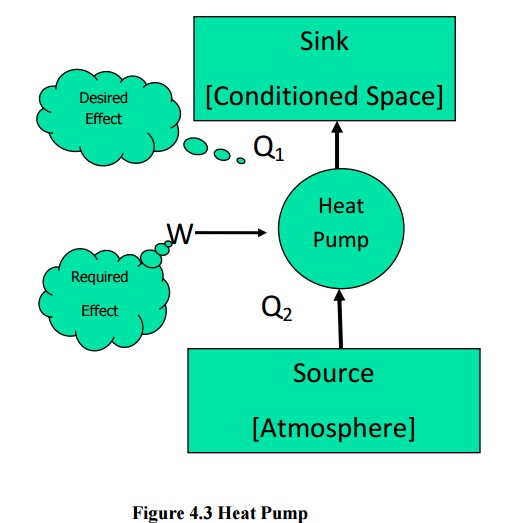
Similarly
for a heat pumps (Figure 4.3)

Related Topics