Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering Thermodynamics : The Second Law of Thermodynamics
Solved Problems: Thermodynamics Second Law
1. Two kg of air at
500kPa, 80°C expands adiabatically in a closed system until its volume is
doubled and its temperature becomes equal to that of the surroundings which is
at 100kPa and 5°C.
For this process, determine
1) the
maximum work
2) the
change in a availability and
3) the
irreversibility.
Take, Cv = 0.718 KJ/kg K, R =
0.287 KJ/kg K.
2. A
reversible heat engine receives 3000 KJ of heat from a constant temperature
source at 650 K . If the surroundings is at 295 K,
determine
i) the
availability of heat energy
ii) Unavailable
heat.
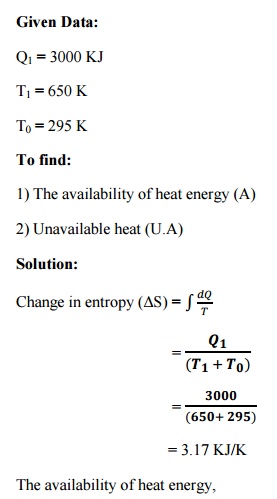
A
= Q1 –T0 (ΔS)
= 3000
–295 (3.17)
= 2064.85
KJ.
Unavailable heat (U.A) = T0 (ΔS)
= 295
(3.17)
= 935.15
KJ.
Result:
1) The
availability of heat energy (A) = 2064.85 KJ.
2) Unavailable
heat (U.A) = 935.15 KJ.
3. Air in a closed
vessel of fixed volume 0.15 m3 exerts pressure of 12 bar at 250 °C.
If the vessel is cooled so that the pressure falls to 3.5 bar , determine the
final pressure, heat transfer and change of entropy.
Given Data:
V1 = 0.15 m3
p1 = 12 bar
= 1200 KN/m2 p2 = 3.5 bar = 350 KN/m2
T1 = 250°C = 273+250 = 523 K
To find:
1) The
final pressure,
2) Heat
transfer
3) Change
of entropy.
Solution:
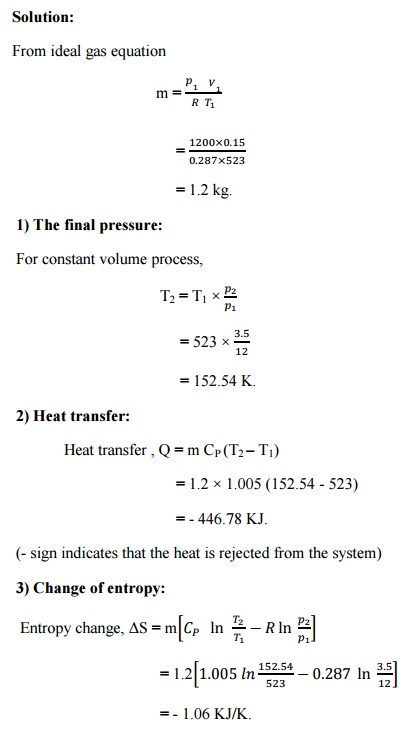
Result:
1) The
final pressure, T2 = 152.54 K.
2) Heat
transfer, Q = - 446.78 KJ.
3) Change
of entropy,-1.06KJ/K. ΔS =
4. A domestic food
freezer maintains a temperature of - 15°C. The ambient air is at 30°C. If the
heat leaks into the freezer at a continuous rate of 1.75 KJ/s, what is the
least power necessary to pump the heat out continuously?
Given Data:
TL = - 15°C = 273 –15 = 258 K
TH = 30°C
= 273 + 30 = 303 K
QS = 1.75 KW
To find:
Least power, (W)
Solution:
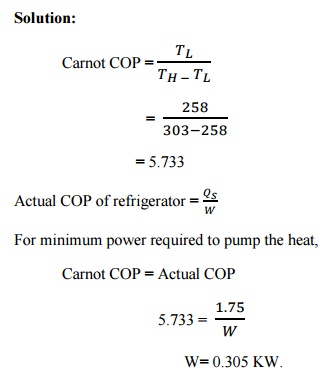
Result:
Least power necessary to pump heat, W = 0.305 KW.
5. A refrigerator
working on reversed Carnot cycle requires 0.5 KW per KW of cooling to maintain
a temperature of -15°C. Determine the following:
a) COP
of the refrigerator
b) Temperature
at which heat is rejected and
Amount of heat rejected to the
surroundings per KW of cooling.
Given Data:
W = 0.5 KW
Q2 = 1 KW
T2 = -15°C = 273 –15 = 258 K.
To find:
1) COP
of the refrigerator (COP)
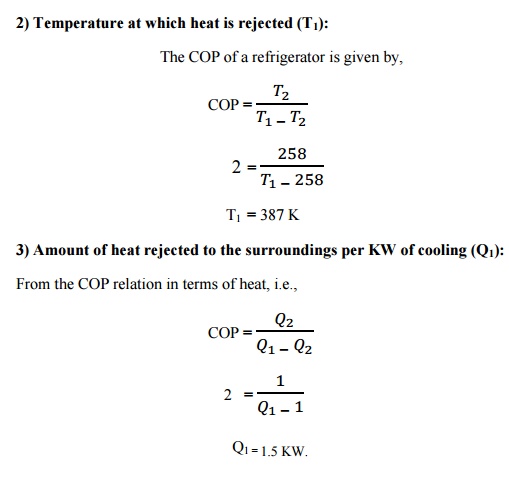
2) Temperature
at which heat is rejected (T1)
3) Amount
of heat rejected to the surroundings per KW of cooling (Q1)
Solution:
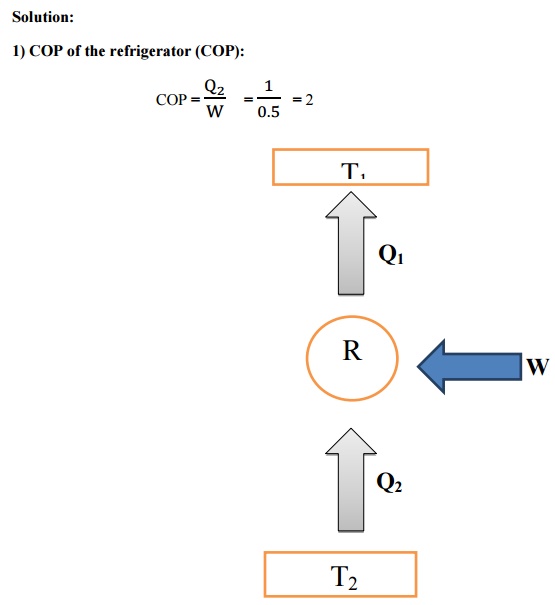
Result:
1) COP
of the refrigerator (COP) = 2
2) Temperature
at which heat is rejected (T1) = 387 K
Amount of heat rejected to the surroundings per KW
of cooling (Q1) = 1.5 KW.
Related Topics