Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Patients with Endocrine Disease
The Parathyroid Glands Physiology
The Parathyroid Glands
Physiology
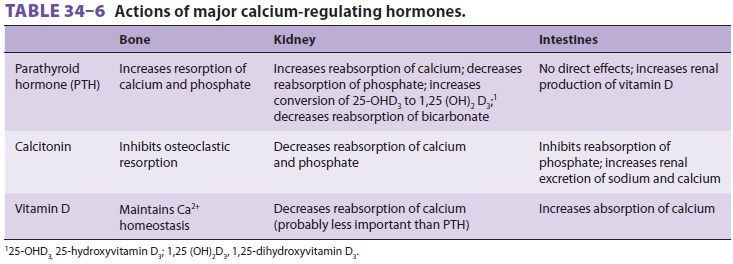
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is the principal
regu-lator of calcium homeostasis. It increases serum calcium concentrations by
promoting resorption of bone and teeth, limiting renal excretion of calcium,
and indirectly enhancing gastrointestinal absorp-tion by its effect on vitamin
D metabolism. PTH decreases serum phosphate by increasing renal excretion. The
effects of PTH on calcium serum levels are countered in lower animals by
calcito-nin, a hormone excreted by parafollicular C-cells in the thyroid, but a
physiological calcium-lowering effect for calcitonin has not been demonstrated
in humans (Table 34–6). Of total body
calcium, 99% is in the skeleton. Of the calcium in the blood, 40% is bound to
proteins and 60% is ionized or complexed to organic ions. Unbound ionized
calcium is physi-ologically the most important fraction.
Related Topics