Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Patients with Endocrine Disease
Anesthesia for Hypoparathyroidism
HYPOPARATHYROIDISM
Clinical Manifestations
Hypoparathyroidism is usually due to deficiency of PTH following
parathyroidectomy. Clinical
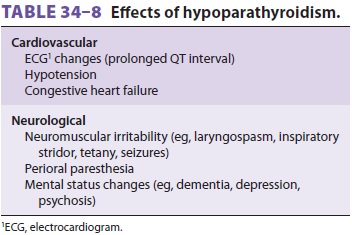
manifestations of hypoparathyroidism are a
result of hypocalcemia ( Table 34–8),
which can also be caused by kidney failure, hypomagnesemia, vitamin D
deficiency, and acute pancreatitis . Hypoalbuminemia decreases total serum
calcium (a 1 g/dL drop in serum albumin causes a 0.8 mg/dL decrease in total
serum calcium), but ionized cal-cium, the active entity, is unaltered. The
archetypi-cal presentation of hypocalcemia is tetany, classically diagnosed by
Chvostek’s sign (painful twitching of the facial musculature following tapping
over the facial nerve) or Trousseau’s sign (carpal spasm fol-lowing inflation
of an arm tourniquet above sys-tolic blood pressure for 3 min). These signs are
also occasionally present in nonhypocalcemic persons. Treatment of symptomatic
hypocalcemia consists of intravenous administration of calcium salts.
Mild hypocalcemia is common following car-diopulmonary bypass or
infusion of albumin solu-tions. In many adult patients this need not be treated
as the response of the PTH–vitamin D axis will usu-ally be sufficient to
restore ionized calcium to nor-mal values and mild hypocalcemia will usually
have no hemodynamic consequences.
Anesthetic Considerations
Serum calcium should be normalized in any patient who presents with
cardiac manifestations of severe hypocalcemia. Alkalosis from hyperventilation
or sodium bicarbonate therapy will further decrease ionized calcium. Although
citrate-containing blood products usually do not lower serum calcium
sig-nificantly, they should be administered cautiously in patients with preexisting
hypocalcemia. Otherconsiderations include avoiding the use of albumin solutions
(which bind and reduce ionized calcium concentrations) and being mindful of the
possibility of coagulopathy.
Related Topics