Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Anesthetic Management: Anesthesia for Patients with Endocrine Disease
The Pancreas Physiology
The Pancreas
Physiology
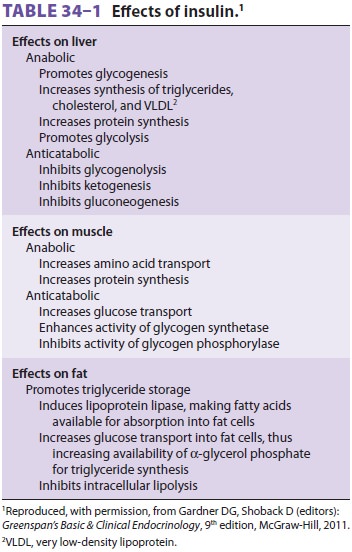
Adults normally secrete approximately 50 units of insulin each day from
the β cells of the islets of
Langerhans in the pancreas. The rate of insulin secretion is primarily
determined by the plasma glucose concentration. Insulin, the most important
anabolic hormone, has multiple metabolic effects, including facilitating
glucose and potassium entry into adipose and muscle cells; increasing glycogen,
protein, and fatty acid synthesis; and decreasing gly-cogenolysis,
gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis, lipolysis, and protein catabolism.
In general, insulin stimulates anabolism,
whereas lack of insulin is associated with catabolism and a negative nitrogen
balance ( Table 34–1).
Related Topics