Chapter: Mechanical : Heat and Mass Transfer : Phase Change Heat Transfer and Heat Exchangers
The Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient
The Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient
The
determination of the overall heat transfer coefficient is an essential, and
often the most uncertain, part of any heat exchanger analysis. We have seen
that if the two fluids are separated by a plane composite wall the overall heat
transfer coefficient is given by:
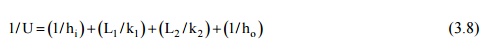
If the two fluids are
separated by a cylindrical tube (inner radius ri, outer radius r0),
the overall heat transfer coefficient is obtained as:
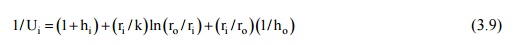
where hi,
and ho are the convective heat transfer coefficients at the inside
and outside surfaces and V, is the overall heat transfer coefficient based on
the inside surface area. Similarly, for the outer surface area, we have:
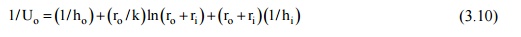
and
U i Ai will be
equal to U o Ao ; or,
Ui ri =U
o ro .
The effect of scale
formation on the inside and outside surfaces of the tubes of a heat exchanger
would be to introduce two additional thermal resistances to the heat flow path.
If hsi and hso are the two heat transfer coefficients due
to scale formation on the inside and outside surface of the inner pipe, the
rate of heat transfer is given by
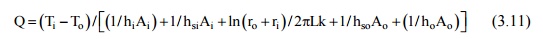
where Ti,
and To are the temperature of the fluid at the inside and outside of
the tube. Thus, the overall heat transfer coeffiCIent based on the inside and
outside surface area of the tube would be:
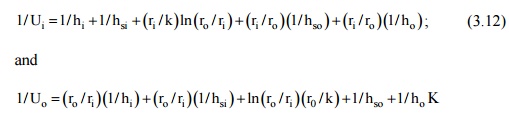
Related Topics