Chapter: Medical Immunology: Immunoglobulin Structure
The Immunoglobulin Superfamily of Proteins
THE IMMUNOGLOBULIN SUPERFAMILY OF PROTEINS
The existence of globular “domains” (Fig. 5.8) is considered as the structural hallmark of immunoglobulin structure. A variety of other proteins that exhibit amino acid sequence ho-mology with immunoglobulins also contain Ig-like domains (Fig. 5.9).
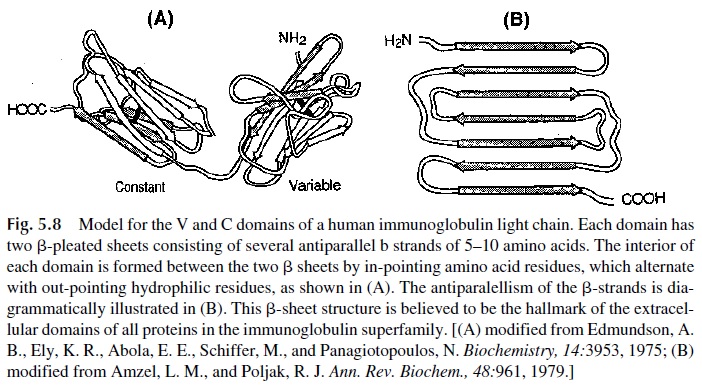
Such proteins are considered as members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, based on the assumption that the genes that encode them must have evolved from a common ancestor gene coding for a single domain, much like the gene coding for the Thy-1 molecule found on murine lym-phocytes and brain cells.
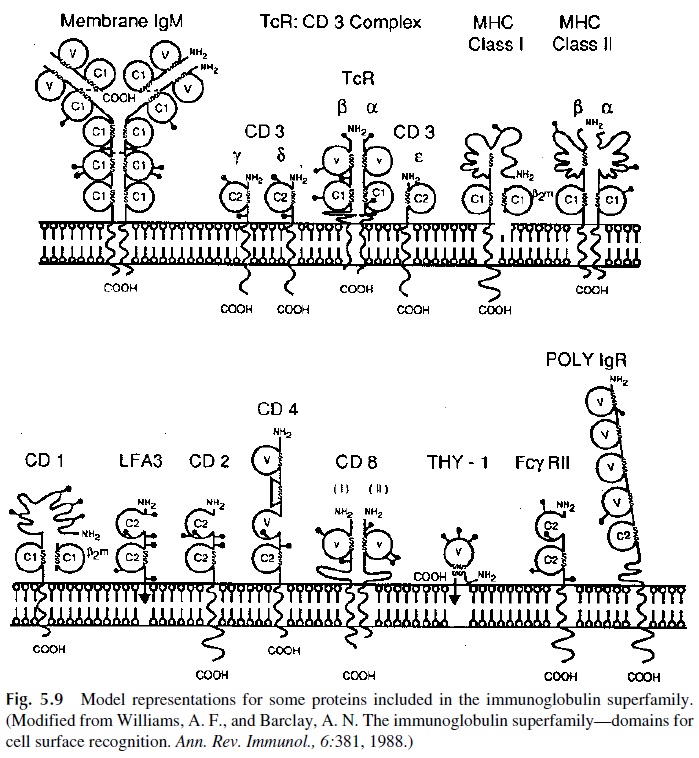
The majority of the membrane proteins of the immunoglobulin superfamily seem to be functionally involved in recognition of specific ligands, which may determine cell-cell contact phenomena and/or cell activation. The T-cell antigen receptor molecule, the major histocompatibility antigens, the polyimmunoglobulin receptor on mucosal cells (see be-low), and the CD2 molecule on T lymphocytes are a few exam-ples of proteins included in the immunoglobulin superfamily.
Related Topics