Chapter: Medical Immunology: Immunoglobulin Structure
Immunoglobulin A: A Molecularly Heterogeneous Immunoglobulin
IMMUNOGLOBULIN A: A MOLECULARLY HETEROGENEOUS IMMUNOGLOBULIN
Serum IgA is molecularly heterogeneous, comprised of a mixture of monomeric, dimeric, and larger polymeric molecules. In a normal individual, over 70–90% of serum IgA is monomeric. Monomeric IgA is similar to IgG, consisting of two heavy chains (α ) and two light chains (k or l ). The dimeric and polymeric forms of IgA found in circulation are co-valently bonded synthetic products containing J chains.
IgA is the predominant immunoglobulin in secretions. Secretory IgA molecules are most frequently dimeric, contain a J chain, as do all polymeric immunoglobulin molecules, and in addition contain a unique polypeptide chain, the secretory component (SC) (Fig. 5.11). A single polypeptide chain of approximately 70,000 daltons, with five homologous
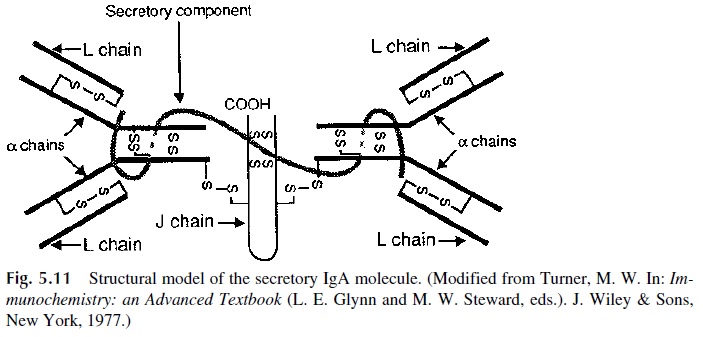
It is synthesized by epithe-lial cells in the mucosa and by hepatocytes, initially as a larger membrane molecule known as polyimmunoglobulin receptor, from which SC is derived by proteolytic cleavage sepa-rating SC from the intramembrane and cytoplasmic segments of its membrane form .
Related Topics