Chapter: 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 9 : Controlling
Techniques of Controlling
Techniques of Controlling
1. Budget and Budgetary Control
A budget is a
tool which helps the management in planning and controlling the business
activities. A budget is an estimate of expected results expressed in numerical
terms. There are various types of budgets like;
·
Sales budget,
·
Purchase budget,
·
Production budget,
·
Fixed budget,
·
Flexible budget,
·
Cash budget,
·
Zero base budget etc
Budgetary Control
is a system of control whereby budgets are prepared for future period and
compared with the actual results for finding out the variations. Corrective
actions are taken in case of deviations.
2. Break – Even point Analysis (BEP)
It is the tool used to analyse the Cost –
Volume – Profit relationships. BEP is the point at which there no profit no
loss. In this point the total costs are recovered. If the sales go up beyond
the break even point , organisation makes profit. If they come down , it may
secure loss.
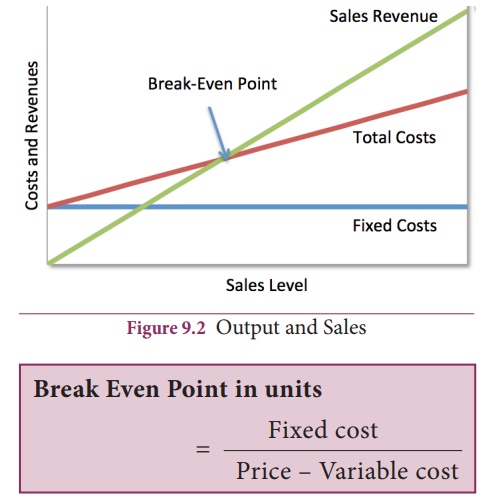
Break even
point is used to take decision regarding price for the marketers.
3. Return on
Investment ( ROI ) – Return on Investment is one of the ratio used as a tool
for measuring the overall efficiency of the firm. It shows the relationship
between profits ( after interest and tax ) and the proprietors fund.
ROI = Net Profit (after interest
and tax) / Share holder fund
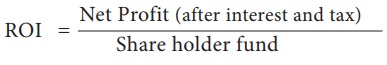
It is a
powerful managerial technique.
4. Statistical
Analysis – Statistical tools such as Percentages, averages, correlation, trend
analysis etc are useful for analysis. This Statistical tools are set as
standard and to find out the deviations and to find out the persons responsible
for such deviations. This helps in controlling.
5. Management
information System (MIS) – Management Information system can be defined as a
systematic procedure to provide relevant information in right time, in right
format to all levels of management for taking decision in business regarding
inventory level , wage payment etc . The information are useful for planning ,
decision making and control.
6. External and
Internal audit – External audit is done by qualified Chartered Accountant. The
object of external audit is to ensure that there is no manipulation in
accounts. After examining the accounting statements of the company the auditor
certifies it.
Internal audit
is done by the companies own staff. The audit ensures that there is no
manipulation in accounts.
7. Responsibility
Centre–Responsibility centre may be defined as any organisational unit under
the charge of a single person who is responsible for its operations. Budgetary
control system are arranged in proper order with the responsibility centre of
the organisation. There are four types of Responsibility Centres. They are,
a) Cost Centre – It is responsible
for controlling the cost. Generally the manager of cost centre is responsible
for salaries, supplies and other costs. Departments like accounting, research
and development, human resources and other staff function comes under cost
centres.
b) Revenue
Centre – The revenue centre may be defined as responsibility centre wherein the
managers are responsible for income in the organisation. Marketing and sales
department are organised as revenue centre.
c) Profit Centre–A
profit centre is usually a self contained organisational unit. It can control
its own cost and revenue. Many large corporations are divided into product
division with each division servicing as a profit centre for its product.
d) Investment
Centre – In this centre the manager is responsible for ascertaining the return
on investment of assets.
8. Personal Observation
– It is a
common technique used
in controlling. It cannot be used as a main control technique. In this
method the managers are expected to see whether the employees are doing what
they are expected to do. This technique is commonly used in small and medium
size concern.
9. PERT and
CPM – Programme Evaluation and Review Techniques (PERT) was developed in 1950s
by the US Navy’s project division. It describes the basic network techniques
which includes Planning, Monitoring and Controlling the project. It is applied
in aerospace and industrial projects. PERT is a statistical tool used to reduce
both time and cost required to complete the project
Critical Path Method (CPM) was
develop by E.I Dupont de Nemours company in 1956 to aid in the scheduling of
routine plant overhaul, maintenance and construction work. Critical path method
is determent by identifying the longest stretch of department activities and
measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish.
Related Topics