Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Exploring java.lang
System - java.lang
System
The System class holds a collection of static methods and variables.
The standard input, output, and error output of the Java run time are stored in
the in, out, and err variables.
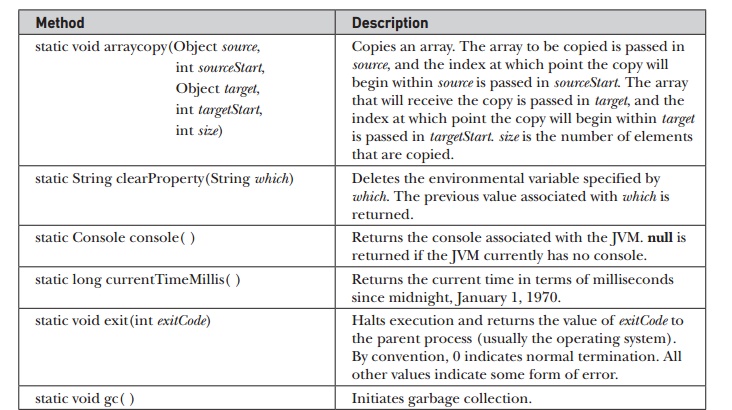
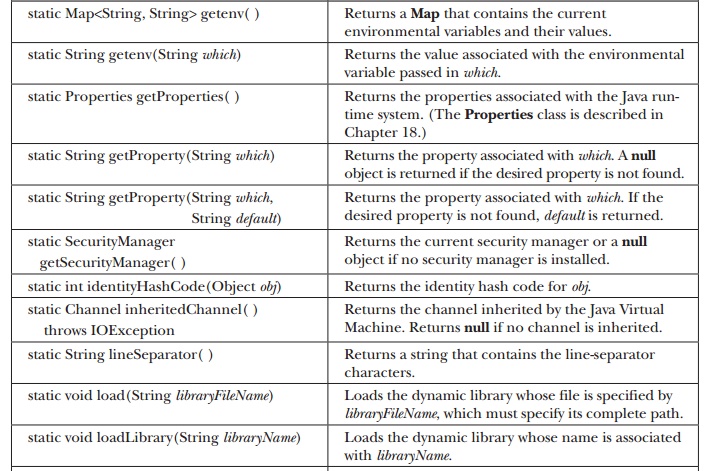
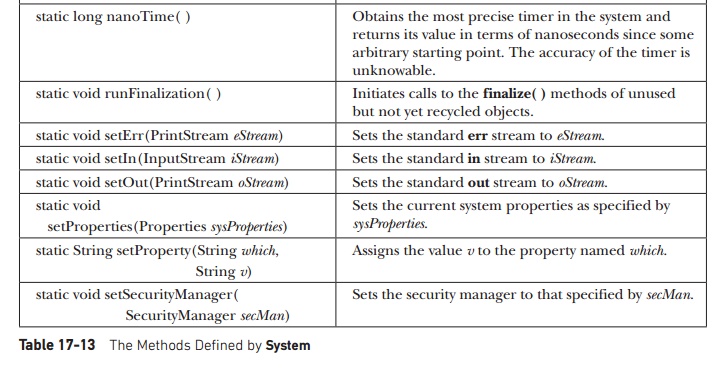
The methods defined by System are
shown in Table 17-13. Many of the methods throw a SecurityException if the operation is not permitted by the security
manager.
Let’s look at some common
uses of System.
Using
currentTimeMillis( ) to Time Program Execution
One use of the System class that you might find
particularly interesting is to use the currentTimeMillis(
) method to time how long various parts of your program take to execute. The currentTimeMillis( ) method returns the current time in terms of
milliseconds since midnight, January 1, 1970. To time a section of your
program, store this value just before beginning the section in question.
Immediately upon completion, call currentTimeMillis(
) again. The elapsed time will be the ending time minus the starting time.
The following program demonstrates this:
// Timing program execution.
class Elapsed {
public static void main(String args[]) { long
start, end;
System.out.println("Timing a for loop from
0 to 100,000,000");
// time a for loop from 0 to 100,000,000
start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // get
starting time
for(long i=0; i < 100000000L; i++) ;
end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // get ending
time
System.out.println("Elapsed time: " +
(end-start));
}
}
Here is a sample run
(remember that your results probably will differ):
Timing a for loop from 0 to 100,000,000
Elapsed time: 10
If your system has a timer
that offers nanosecond precision, then you could rewrite the preceding program
to use nanoTime( ) rather than currentTimeMillis( ). For example, here
is the key portion of the program rewritten to use nanoTime( ):
start = System.nanoTime(); // get starting time
for(long i=0; i < 100000000L; i++) ;
end = System.nanoTime(); // get ending time
Using
arraycopy( )
The arraycopy( ) method can be used to copy quickly an array of any
type from one place to another. This is much faster than the equivalent loop
written out longhand in Java. Here is an example of two arrays being copied by
the arraycopy( ) method. First, a is copied to b. Next, all of a’s
elements are shifted down by one.
Then, b is shifted up by one.
// Using arraycopy().
class ACDemo {
static byte a[] = { 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71,
72, 73, 74 }; static byte b[] = { 77, 77, 77, 77, 77, 77, 77, 77, 77, 77 };
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("a = " + new
String(a));
System.out.println("b = " + new
String(b));
System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, a.length);
System.out.println("a = " + new
String(a));
System.out.println("b = " + new
String(b));
System.arraycopy(a, 0, a, 1, a.length - 1);
System.arraycopy(b, 1, b, 0, b.length - 1);
System.out.println("a = " + new
String(a));
System.out.println("b = " + new
String(b));
}
}
As you can see from the
following output, you can copy using the same source and destination in either direction:
a = ABCDEFGHIJ b = MMMMMMMMMM a = ABCDEFGHIJ b
= ABCDEFGHIJ a = AABCDEFGHI b = BCDEFGHIJJ
Environment
Properties
The following properties are
available in all cases:
file.separator
java.class.path
java.class.version
java.compiler
java.ext.dirs
java.home
java.io.tmpdir
java.library.path
java.specification.name
java.specification.vendor
java.specification.version
java.vendor
java.vendor.url
java.version
java.vm.name
java.vm.specification.name
java.vm.specification.vendor
java.vm.specification.version
java.vm.vendor
java.vm.version
line.separator
os.arch
os.name
os.version
path.separator
user.dir
user.home
user.name
You can obtain the values of
various environment variables by calling the System.getProperty( ) method. For example, the following program
displays the path to the current
user directory:
class ShowUserDir {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
}
Object
As mentioned in Part I, Object is a superclass of all other
classes. Object defines the methods
shown in Table 17-14, which are available to every object.
Related Topics