Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Exploring java.lang
Package, StackTraceElement, Enum - java.lang
Package
Package encapsulates version data associated with a package. Package version information is becoming more important because of
the proliferation of packages and because a Java program may need to know what
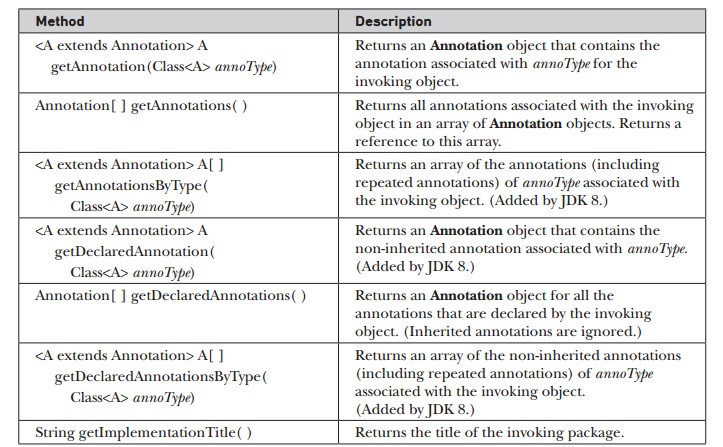
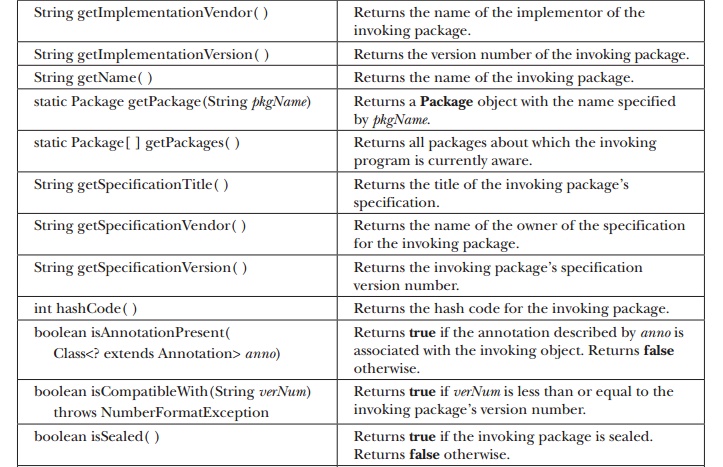
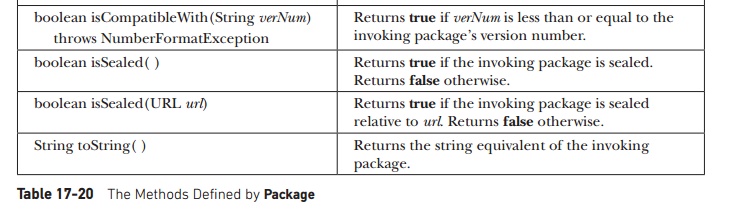
version of a package is available. The methods defined by Package are shown in Table 17-20. The following program
demonstrates Package, displaying the packages about which the program
currently is aware:
// Demonstrate Package
class PkgTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Package pkgs[];
pkgs = Package.getPackages();
for(int i=0; i < pkgs.length; i++)
System.out.println(
pkgs[i].getName() + " " +
pkgs[i].getImplementationTitle() + " " +
pkgs[i].getImplementationVendor() + "
" + pkgs[i].getImplementationVersion()
);
}
}
RuntimePermission
RuntimePermission relates to Java’s security mechanism and is not
examined further here.
Throwable
The Throwable class supports Java’s exception-handling system and is
the class from which all exception classes are derived. It is discussed in
Chapter 10.
SecurityManager
SecurityManager supports Java’s security system. A reference to
the current security manager can be
obtained by calling getSecurityManager(
) defined by the System class.
StackTraceElement
The StackTraceElement class describes a single stack frame, which is an individual element of a stack trace when
an exception occurs. Each stack frame represents an execution point, which includes such things as the name of the
class, the name of the method, the name of the file, and the source-code line
number. An array of StackTraceElements
is returned by the getStackTrace( )
method of the Throwable class.
StackTraceElement has one constructor:
StackTraceElement(String className, String methName, string fileName,
int line)
Here, the name of the class
is specified by className, the name
of the method is specified in methName,
the name of the file is specified by
fileName, and the line number is passed in line. If there is no
valid line number, use a negative value for line.
Furthermore, a value of –2 for line indicates
that this frame refers to a native method.
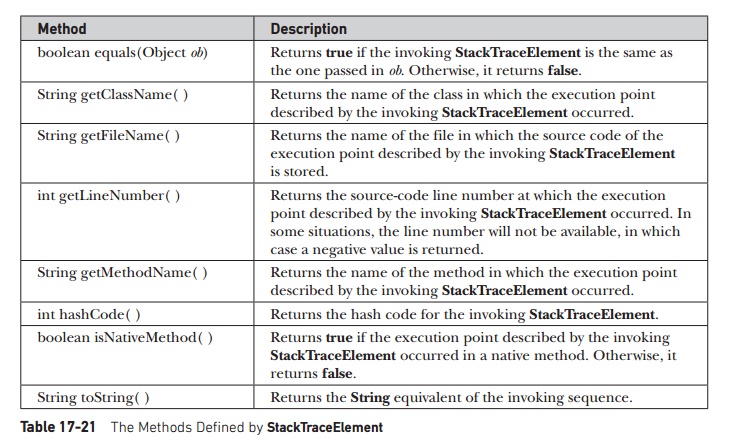
The methods supported by StackTraceElement are shown in Table
17-21. These methods give you programmatic access to a stack trace.
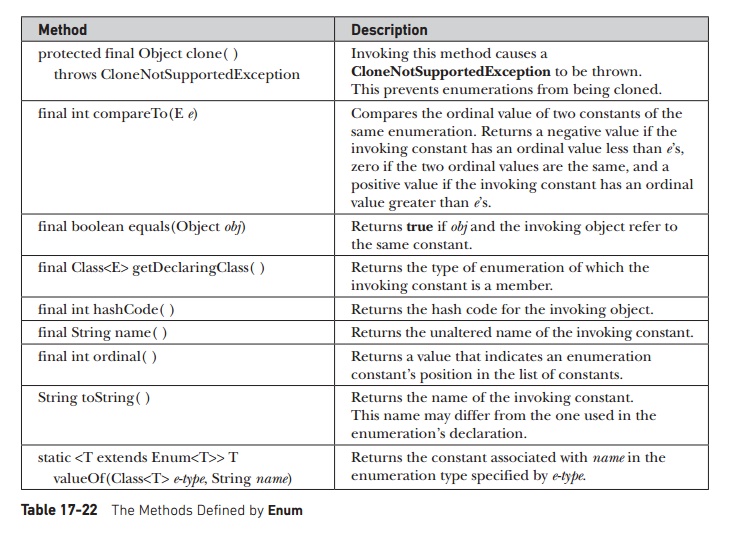
Enum
As described in Chapter 12,
an enumeration is a list of named constants. (Recall that an enumeration is
created by using the keyword enum.)
All enumerations automatically inherit Enum.
Enum is a generic class that is
declared as shown here:
class Enum<E extends
Enum<E>>
Here, E stands for the enumeration type. Enum has no public constructors.
Enum defines several methods that are available for use by all
enumerations, which are shown in
Table 17-22.
ClassValue
ClassValue can be used to associate a value with a type. It is a generic type
defined like this: Class
ClassValue<T>
It is designed for highly
specialized uses, not for normal programming.
Related Topics