Chapter: Security in Computing : Cryptography Explained
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption
We were introduced to
symmetric encryption in Chapter 2. Here
we review the two fundamentals of symmetric encryption, confusion and
diffusion, as they are represented in modern algorithms. We also review
cryptanalysis so that we can appreciate how encryption can fail. Finally, we
study the details of the two main symmetric systems, DES and AES. We also
introduce three other fairly common schemes: RC2, RC4, and RC5.
Fundamental Concepts
To refresh your memory and
prepare you for a detailed description of DES and AES, we present here a review
of important points from Chapter 2.
Confusion and Diffusion; Substitution and Permutation
Recall from Chapter 2 that confusion is the act of creating
ciphertext so that its corresponding plaintext is not apparent. Substitution is
the basic tool for confusion; here, we substitute one element of ciphertext for
an element of plaintext in some regular manner. Substitution is also the point
at which a key is typically introduced in the process. As we noted in Chapter 2, single substitutions can be fairly
easy to break, so strong encryption algorithms often employ several different
substitutions.
Diffusion is the act of spreading the effect of a change in the plaintext throughout the resulting ciphertext. With poor diffusion, a change to one bit in the plaintext results in a change to only one bit in the ciphertext. A cryptanalyst might trace single bits backward from ciphertext to plaintext, having the effect of reducing 2n possibilities in an n-bit ciphertext to just n, and thereby reducing the cryptanalytic complexity from exponential to linear. This reduction is not desirable; we always want to make the cryptanalyst work as hard as possible.
Substitution is sometimes
represented by so-called S-boxes, which are nothing other than table-driven
substitutions. Diffusion can be accomplished by permutations, or
"P-boxes." Strong cryptosystems may use several iterations of a
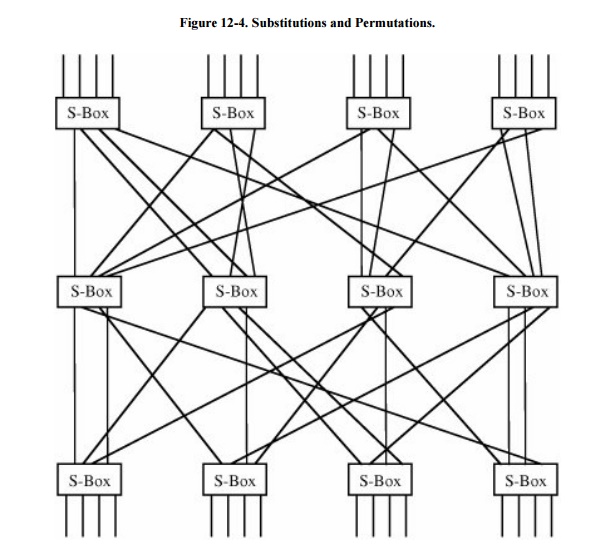
substitute-permute cycle. Such a cycle is shown in Figure
12-4. In the figure, a line entering an S-box from the top undergoes
a substitution in the box. Then it is sent to another S-box in the line below
by permutation of the order in some way; this permutation is represented by the
lines spreading out at many angles.
Problems of Symmetric Key Systems
Symmetric key systems present
several difficulties.
As with all key systems, if the key is revealed (stolen, guessed,
bought, or otherwise compromised), the interceptors can immediately decrypt all
the encrypted information they have available. Furthermore, an impostor using
an intercepted key can produce bogus messages under the guise of a legitimate
sender. For this reason, in secure encryption systems, the keys are changed
fairly frequently so that a compromised key will reveal only a limited amount
of information.
Distribution of keys becomes
a problem. Keys must be transmitted with utmost security since they allow
access to all information encrypted under them. For applications that extend
throughout the world, this can be a complex task. Often, couriers are used to
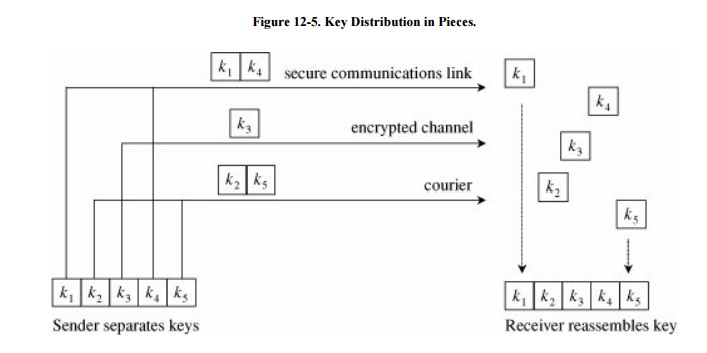
distribute the keys securely by hand. Another approach is to distribute the
keys in pieces under separate channels so that any one discovery will not
produce a full key. (For example, the Clipper program in the United States uses
a 2-piece key distribution.) This approach is shown in Figure 12-5.
As described earlier, the
number of keys increases with the square of the number of people exchanging
secret information. This problem is usually contained by having only a few
people exchange secrets directly so that the network of interchanges is
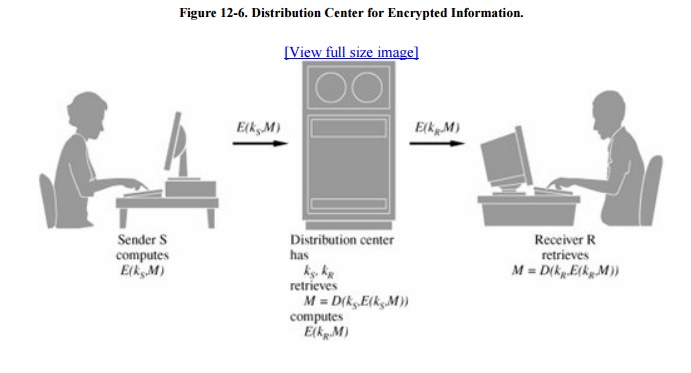
relatively small. If people in separate networks need to exchange secrets, they
can do so through a central "clearing house" or "forwarding
office" that accepts secrets from one person, decrypts them, reencrypts
them using another person's secret key, and transmits them. This technique is
shown in Figure 12-6.
Related Topics