different stages or processes - Sulphur Cycle | 11th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Agricultural Microbiology
Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Agricultural Microbiology
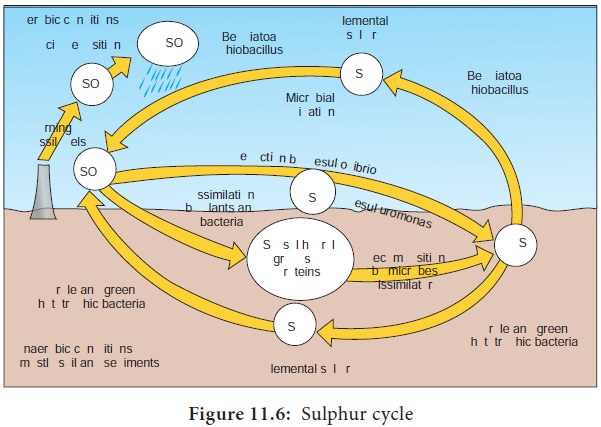
Sulphur Cycle
Sulphur Cycle
Sulphur is present in sulphur containing aminoacids. The sulphur
cycle involves oxidation – reduction reaction between Sulphate (SO4),
Elemental S and H2S and hence there is change in the valence states
of sulphur from -2 to +6.
The basic steps involved in sulphur cycle are
1.
Sulphide/ sulphur oxidation
2. Sulphate reduction
3.
Sulphur reduction
4.
Organicsulphur compound oxidation or reduction
5.
Desulfurylation
Sulphide/Sulphur oxidation (H2S→S0→SO42-)
It is carried out by prokaryotes under aerobic and anaerobic
conditions. Under aerobic conditions, H2S is spontaneously oxidized
at neutral pH to elemental sulphur. Elemental sulphur is oxidized to suphates
by chemolithotrophic bacteria like Thiobacillus,
Beggiatoa.
If light is available, H2S can be used as electron donor to carry out photosynthesis under anoxic conditions by phototrophic sulphur bacteria like Chromatium and Chlorobium.
Sulphate reduction
When sulphate is present in habitats, different groups of
microorganisms are capable of carrying out sulphate reduction.
Beijerinck described the use of sulphate (SO42-)
as a terminal electron acceptor during anaerobic respiration to form sulphide
(H2S). This process is called Dissimilatory Sulphate
Reduction(DSR). The anerobic bacteria
capable of carrying out DSR are Desulfovibrio,
Desulfococcus, Desulfotomaculum (Figure
11.6) This reaction by sulphate
reducers requires organic carbon sources like pyruvate or lactate. H2S
accumulated in such habitats by the action of sulphate reducers is toxic to
aerobic organisms.
The reduction of sulphate to H2S, for building up
aminoacids and proteins
is called as
assimilatory sulphate reduction. The H2S
thus produced is immediately
incorporated into organic compounds.
Sulphur reduction (S0→H2S):
The dissimilative sulphur reducing bacteria can reduce elemental
sulphur to hydrogen sulphide. Example: Desulfuromonas,
an obligate anaerobe. Under aerobic
conditions, organisms like Pseudomonas,
Proteus and Salmonella are also capable of performing this
reaction.
Organic sulphur compounds reduction/oxidation
Organic sulphur compounds like dimethyl sulphide can be used as
carbon and energy source for many microorganisms.
Desulfurylation
It is a process where organic sulphur compounds are used up by
microorganisms for energy to produce H2S.
Related Topics