different stages or processes - Carbon Cycle | 11th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Agricultural Microbiology
Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Agricultural Microbiology
Carbon Cycle
Carbon Cycle
Carbon is a macro element present in all living cells. In microorganisms,
they are present in all macromolecules like cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane,
proteins and nucleic acids.
Reservoirs of Carbon:
Reservoirs are the storage places of nutrients that are present
in nature. They store nutrients in large amounts for longer periods of time.
Atmospheric CO2, dissolved carbon in oceans and
freshwater, organic matter are actively cycled carbon reservoirs. Sediments and
fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas are slowly cycled carbon
reservoirs. Carbon is cycled between these reservoirs by the biochemical
activities of micro organisms and other living things (Figure 11.1).
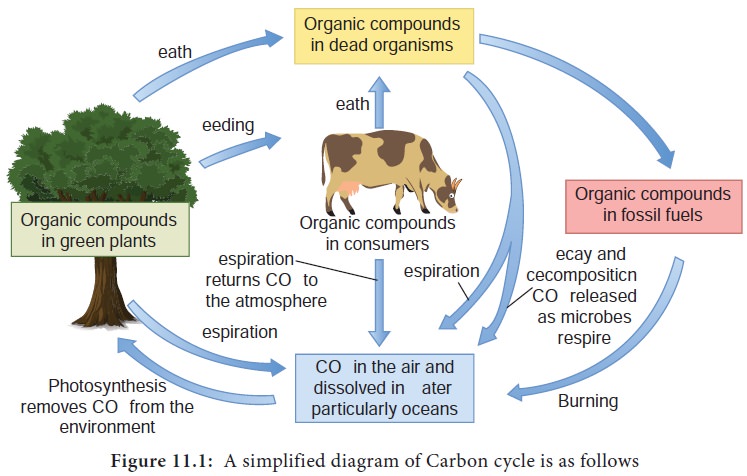
The different stages or processes involved in carbon cycle are
1. Photosynthesis
2. Decomposition
3. Methanogenesis
1. Photosynthesis
It is a process where atmospheric CO2 is converted to organic carbon (CH2O)n. This is carried out by higher plants, photosynthetic bacteria, cyanobacteria and algae using radiant energy from the sun. This can be explained by the equation,
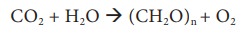
where (CH2O)n represents the organic form
of carbon (Example: Carbohydrates) which gets incorporated into the
photosynthetic organisms. This organic carbon serves as food for herbivores and
in turn for carnivores.
2. Decomposition
The organic matter fixed as a result of photosynthesis is
eventually degraded by microorganisms to CO2 during processes like
respiration and decomposition. When aerobic and anaerobic organisms respire, CO2
is released into the atmosphere. Much of the CO2 is released when
dead organisms decompose in the soil predominantly by the activities of soil
microorganisms. Burning of fossil fuels also release CO2 into the
atmosphere.
3. Methanogenesis
It is an anaerobic process where CO2 gets converted to
CH4 (methane) by strict anaerobes like methanogens (Example: Methanobacterium). Methanogens are a group of Archaebacteria found in
anaerobic environments like swamps, marshes, rumen of ruminants, paddy fields
and gut of termites.
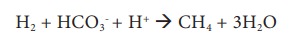
Methane is converted back to carbondioxide by a process called Methylotrophy.
Related Topics