Cell Biology | Term 2 Unit 4 | 7th Science - Student Activities | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 4 : Cell Biology
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 4 : Cell Biology
Student Activities
ACTIVITY 1
Do you remember the lesson studied in previous class, how will you find whether on object is living or non – living? Write it down. An object is living or non – living?
1. Form a team and work together to write down some of the functions of life, which you can remember.
2. Do you think that an individual cell is living? Explain your answer
3. Write about various organelles of a cell which you know.
ACTIVITY 2
Find out major organs that are part of the circulatory system of a human body and listout their functions
Heart - It pumps out blood.
Auricles - Upper chambers of the heart
Ventricles - Lower chambers of the heart
Arteries - They carry oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
Veins - They carry oxygen-poor blood back from the body to the heart
Capillaries - They bring nutrients and oxygen to the tissues and remove waste products from the tissues.
Lungs - The alveoli in lungs purify the blood by supplying oxygen and removing CO2 from blood.
ACTIVITY 3
Study the pictures given and write the differences between cells that you observe in the given table.
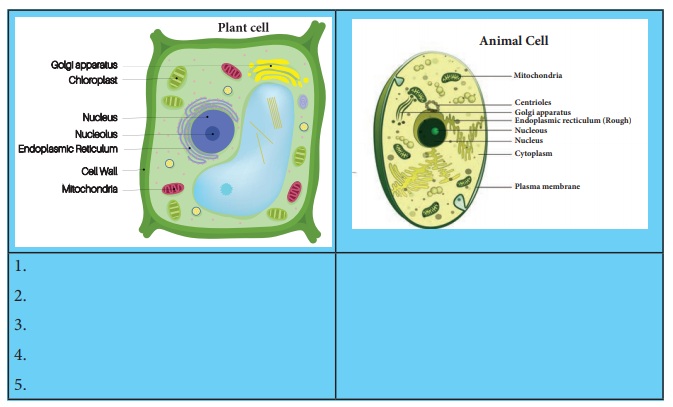
Plant cell
1. Plant cell has a cell wall.
2. It has chloroplast.
3. Centrioles absent
4. One large central vacuole
5. Lysosome usually not evident. Cilia absent in most plant cells.
Animal cell
1. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
2. Does not contain chloroplast.
3. Centrioles present.
4. One or more small vacuoles.
5. Lysosomes occur in cytoplasm. Cilia is present.
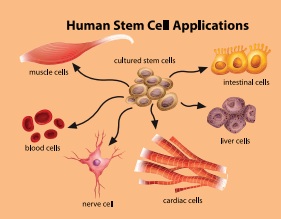
Stem Cells
Stem cells are quite amazing as they can divide and multiply while at the same time with their ability to develop into any other type of cell. Embryonic stem cells are very special as they can become absolutely any type of cell in the body, for example, blood cell, nerve cell, muscle cell or gland cell. So they are utilized by the Scientist and Medicos, to cure and prevent some diseases like Spinal cord injury.
Observing chloroplast in algae
Collect some algae from pond and separate out thin filaments of them. Place a few filaments on a slide. Observe it under the microscope. Take the help of given figure and draw the picture of chloroplast that you have observed under the microscope. Chloroplast is a type of plastid. which are present only in plant cells. Plastids are mainly of two types chromoplasts (coloured) and leucoplasts (colourless).
Various range of these plastids impart different colours to various parts of plant. Chromoplast impart colour to flower and fruits. As fruits ripen, chloroplasts change to chromoplasts. Starch is converted to sugar.
ACTIVITY 4
Summarise what you have learnt
Now you’ve studied the internal structure of a cell. Let us summerise what we have learnt so far Complete this table by filling the main function of each of the cell structures
Cell Structure Function(s) - Function(s)
1. Cell membrane - Allows certain substances to pass in and out of the cell.
2. Cell wall - Provides a frame work for support and stability.
3. Cytoplasm - Area of movement of cell organelles.
4. Mitochondrion - Responsible for cellular transpiration and it releases energy from the food
5. Vacuole - Contains organic and inorganic molecules along with water to support the organelles.
6. Chloroplast - Produces food from sun's energy.
7. Endoplasmic reticulum - Produces protein, lipids and steroids and transports them within the cell.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells do not contain a nucleus. Without a nucleus, these cells die quickly; about two million red blood cells die every second! Luckily, the body produces new red blood cells every day.

Related Topics