Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Excretion
Structure of kidney
Structure of kidney
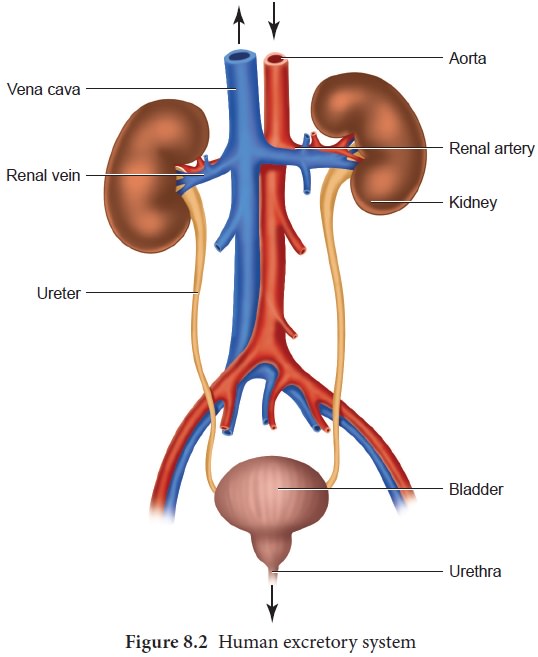
Excretory system in human consists of a pair of
kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder and urethra (Figure. 8.2). Kidneys
are reddish brown, bean shaped structures that lie in the superior lumbar
region between the levels of the last thoracic and third lumber vertebra close
to the dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity. The right kidney is placed
slightly lower than the left kidney. Each kidney weighs an average of 120-170
grams. The outer layer of the kidney is covered by three layers ofsupportive
tissues namely, renal fascia, perirenal fat capsule and fibrous capsule.
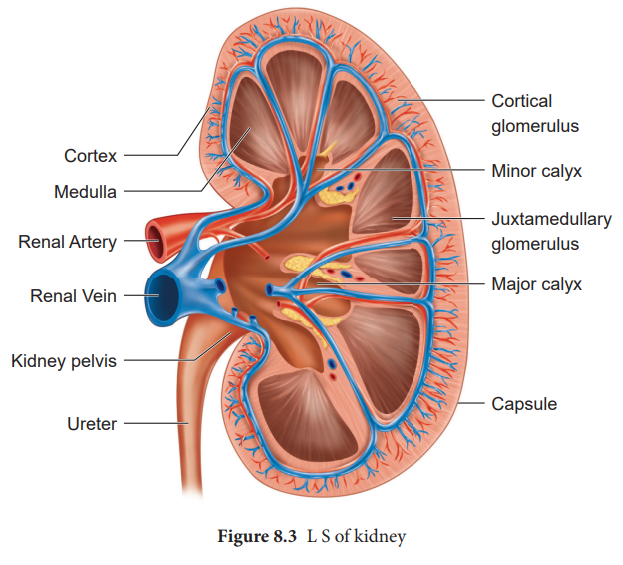
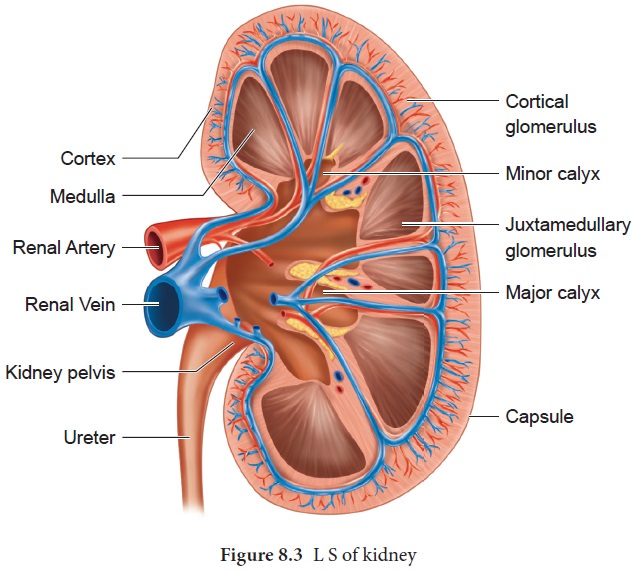
The longitudinal section of kidney (Figure. 8.3)
shows, an outer cortex, inner medulla and pelvis. The medulla is divided into a
few conical tissue masses called medullary pyramids or renal pyramids. The part
of cortex that extends in between the medullary pyramids is the renal columns
of Bertini. The centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney has a notch
called the renal hilum, through which ureter, blood vessels and nerves
innervate. Inner to the hilum is a broad funnel shaped space called the renal pelvis
with projection called calyces.
The renal pelvis is continuous with the ureter once it
leaves the hilum. The walls of the calyces, pelvis and ureter have smooth
muscles which contracts rhythmically. The calyces collect the urine and empties
into the ureter, which is stored in the urinary bladder temporarily. The
urinary bladder opens into the urethra through which urine is expelled out.
Related Topics