Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 5 : Carbohydrates
Structure of Glucose, Fructose and Galactose
Structure of Glucose, Fructose and Galactose
1. Glucose:
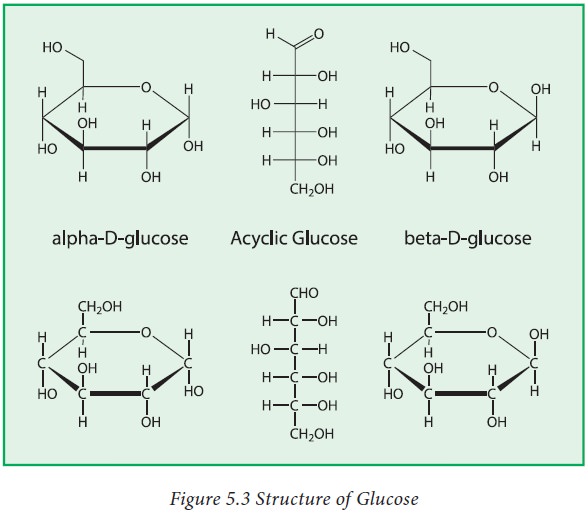
Glucose
has the molecular formula (C6H12O6) and has a
six member ring. Glucose may be represented by the following open chain
structure. But in solution it exists only as a six membered ring structure
called pyranose form. Glucose is known as grape sugar.
2. Fructose
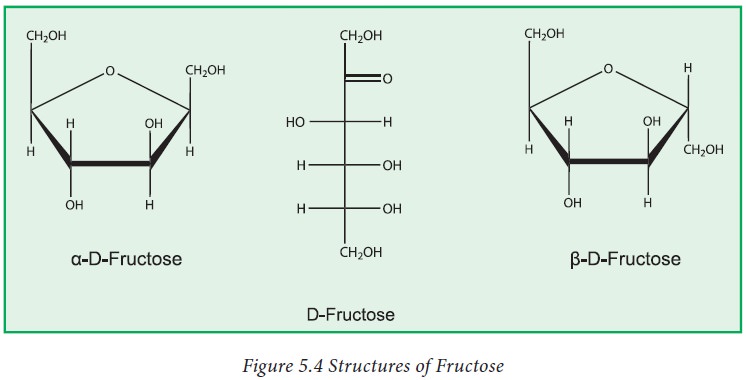
Fructose
has the molecular formula (C6H12O6) and has a
five member ring. Fructose exists mostly as a five membered ring structure
called “furanose form”. Fructose is known as the fruit sugar as its make source
in the diet is fruits and vegetables. Honey is also a good source.
Fructose is more soluble than other
sugars and hard to crystallize because it is more hygroscopic and holds onto
water stronger than the others. This means that fructose can be used to extend
the shelf life of baked products more than other sugars.
3. Galactose
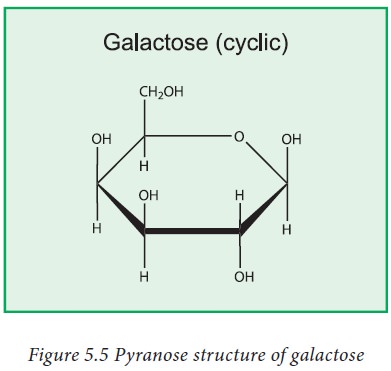
Galactose is a monosaccharide and has
the same chemical formula as glucose, i.e., C6H12O6.
It is similar to glucose in its structure, differing only in the position of
one hydroxyl group. This difference, however, gives galactose different
chemical and biochemical properties to glucose. In solution, it forms 5- and
6-membered rings but also exists in linear form. Small amounts of lactose and
galactose can appear in nondairy foods.
Epimers
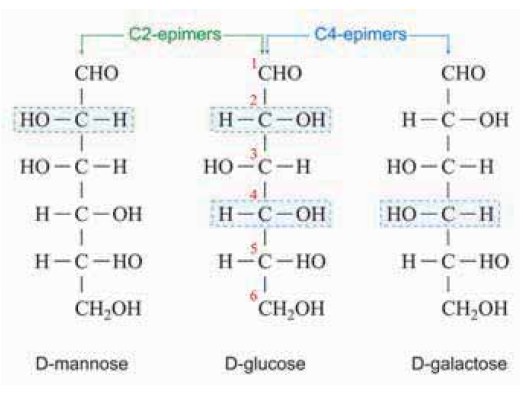
D-sugars differing in configuration
at a single asymmetric center are known as epimers. Thus D-glucose and
D-galactose are epimers at C4 ; D- glucose and D-mannose are epimers at C2.
Anomers:
Sugars differing in configuration at
the C1 asymmetric center are known as anomers. The C1–carbon is called as
anomeric carbon. Thus α-D and β-D forms of glucose are anomers.
Mutarotation:
Mutarotation was discovered by
chemisty dubrunfaut in 1814. Mutorotation is the change in optical rotation due
to change in equilibrium between two anomers.
When D-glucose is crystallized at
room temperature and a fresh solution is prepared, its specific rotation of
polarized light is +112°; but after 12-18 hours it changes to +52.5°. If
initial crystallization is taking place at 98° C and then solubilized, the
specific rotation is found to be +19°, which also changes to +52.5° within few
hours. This change in rotation with time is called mutarotation.
Related Topics