Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 6 : Cell: The Unit of Life
Structure and Functions of the nucleus
Nucleus
![]()
![]()
![]()
Nucleus is an important unit of cell which control
all activities of the cell. Nucleus holds the hereditary information. It is the
largest among all cell organelles. It may be spherical, cuboidal, ellipsoidal
or discoidal.
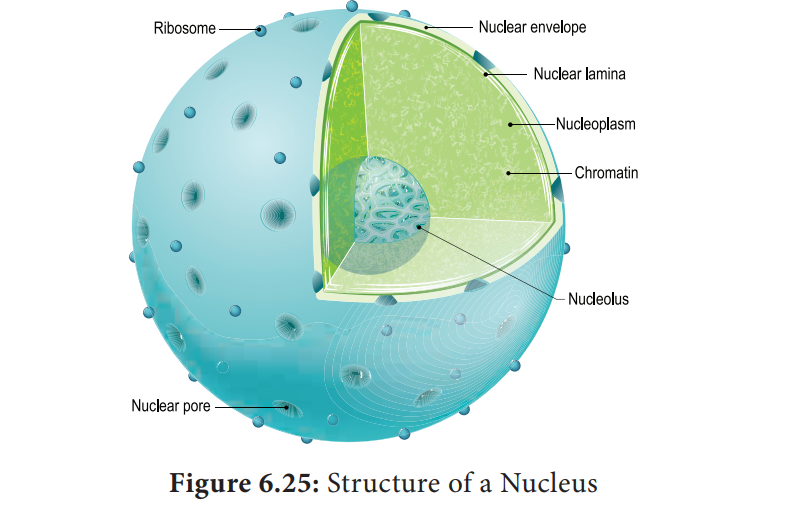
It is surrounded by a double membrane structure called nuclear envelope, which has the inner and outer membrane.
The inner membrane is smooth without ribosomes and the outer membrane is rough
by the presence of ribosomes and is continues with irregular and infrequent
intervals with the endoplasmic reticulum. The membrane is perforated by pores
known as nuclear pores which allows
materials such as mRNA, ribosomal units, proteins and other macromolecules to
pass in and out of the nucleus. The pores enclosed by circular structures
called annuli. The pore and annuli
forms the pore complex . The space
between two membranes is called perinuclear space.
Nuclear space is filled with nucleoplasm, a gelatinous matrix has uncondensed chromatin network and a conspicuous nucleoli. The chromatin network is the uncoiled, indistinct and remain thread
like during the interphase. It has little amount of RNA and DNA bound to
histone proteins in eukaryotic cells (Figure 6.25).
Chromatin is a viscous gelatinous substance that contains DNA, histone & non–histone proteins and RNA. H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are the different histones found in chromatin. It is formed by a series of repeated units called nucleosomes. Each nucleosome has a core of eight histone subunits.
During cell division chromatin is condensed into an
organized form called chromosome.
The portion of Eukaryotic chromosome
which is transcribed into mRNA contains active genes that are not tightly
condensed during interphase is called Euchromatin.
The portion of a Eukaryotic chromosome that is not transcribed into mRNA which
remains condensed during interphase and stains intensely is called Heterochromatin. I Nucleolus is a small, dense, spherical structure either present
singly or in multiples inside nucleus and it’s not membrane bound. Nucleoli
possesses genes for rRNA and tRNA.
Functions of the nucleus
•
Controlling all the cellular activities
•
Storing the genetic or hereditary information.
•
Coding the information in the DNA for the
production of enzymes and proteins.
·
DNA duplication and transcription takes place in
the nucleus.
· In nucleolus ribosomal biogenesis takes place.
Related Topics