Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 6 : Cell: The Unit of Life
Cytological Techniques
Cytological Techniques
1. Preparation of Slides
There are different types of
mounting based on the portion of a specimen to be observed
a. Whole mount: The whole organism or smaller structure is mounted
over a slide and observed.
b. Squash: Is a preparation where the material to be observed is crushed/ squashed on to a slide so as to reveal their contents. Example: Pollen grains, mitosis and meiosis in root tips and flower buds to observe chromosomes.
c. Smears:
Here the
specimen is in the fluid (blood,
microbial cultures etc.,) are scraped, brushed or aspirated from surface of
organ. Example: Epithelial cells.
d. Sections:
Free hand
sections from a specimen and thin
sections are selected, stained and mounted on a slide. Example: Leaf and stem
of plants.
2. Recording the Observations
The observations made through a microscope can be
recorded by hand diagrams or through microphotographs.
Hand
diagrams: Hand diagrams are drawn
using ordinary pencil by observing the slide and drawing manually.
Microphotograph: Images
of structures observed through
microscopes can be further magnified, projected and saved by attaching a camera
to the microscope by a microscope coupler or eyepiece adaptor. Picture taken
using a inbuilt camera in a microscope is called microphotography or microphotograph.
![]()
![]()
![]()
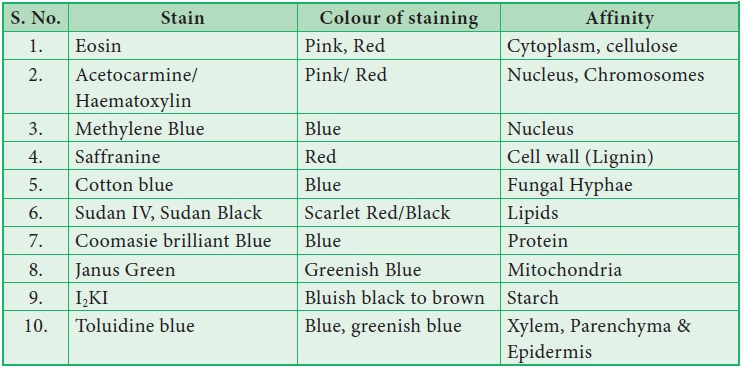
3. Staining Techniques
Stainingisveryimportanttoobservedifferent
components of the cell. Each component of the cell has different affinity
towards different stains. The technique of staining the cells and tissue is
called ‘histochemical staining’ or ‘histochemistry’.
Common stains used in Histochemistry
Related Topics