Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 20 : Breeding and Biotechnology
Stem Cells
Stem Cells
Our body is composed of
over 200 specialised cell types, that can carry out specific functions. e.g.
neurons or nerve cell that can transmit signals, or heart cells which contract
to pump blood or pancreatic cells to secrete insulin. These specialised cells
are called as differentiated cells.
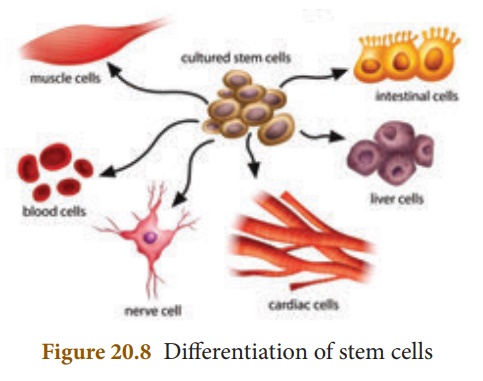
In contrast to
differentiated cells, stem cells are undifferentiated or unspecialised
mass of cells. The stem cells are the cells of variable potency. Potency refers
to the number of possible fates that a cell can acquire. The two important
properties of stem cells that differentiate them from other cells are:
i. its ability to divide
and give rise to more stem cells by self-renewal
ii. its ability to give
rise to specialised cells with specific functions by the process of
differentiation.
Types of stem cells
Embryonic stem cells can be extracted and
cultured from the early embryos. These cells are derived from the inner cell
mass of blastocyst . These cells can be developed into any
cell in the body.
Adult stem cell or somatic stem cell are
found in the neonatal (new born) and adults. They have the ability to
divide and give rise to specific cell types. Sources of adult stem cells are
amniotic fluid, umbilical cord and bone marrow.
Stem-cell therapy
Sometimes cells, tissues
and organs in the body may be permanently damaged or lost due to genetic
condition or disease or injury. In such situations stem cells are used for the
treatment of diseases which is called stem-cell therapy. In treating neurodegenerative
disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease neuronal stem
cells can be used to replace the damaged or lost neurons.
Related Topics