Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 20 : Breeding and Biotechnology
Genetic Engineering
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering is the
manipulation and transfer of genes from one organism to another organisms to
create a new DNA called as recombinant DNA(rDNA). The term recombinant is used
because DNA from two different sources can be joined together. Hence, genetic
engineering is also called as recombinant DNA technology.
1. Techniques of Genetic Engineering – Basic Requirements
Important discoveries
that led to the stepping stone of rDNA technology were
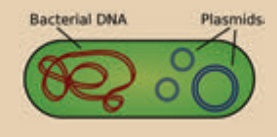
a. Presence of plasmid in bacteria that can undergo
replication independently along with chromosomal DNA.
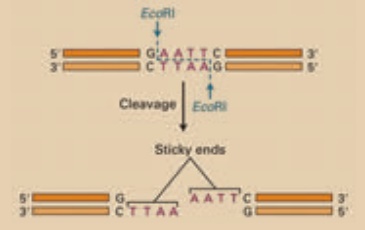
b. Restriction enzymes cuts or break DNA at specific sites and
are also called as molecular scissors.
c. DNA ligases are the enzymes which help in ligating
(joining) the broken DNA fragments.![]()
![]()
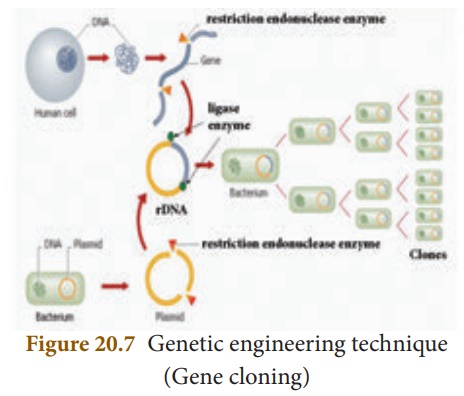
2. Gene Cloning
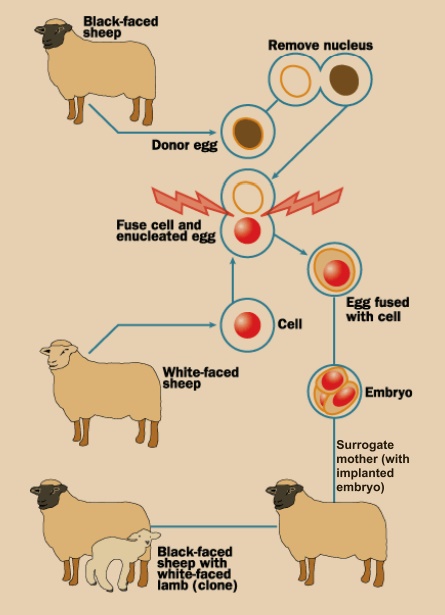
What reminds to your
mind when you hear the word clone? Of course, ‘DOLLY’ the cloned sheep. The
carbon copy of an individual is often called a clone. However, more
appropriately, a clone means to make a genetically exact copy of an organism.
In gene cloning, a gene
or a piece of DNA fragment is inserted into a bacterial cell where DNA will be
multiplied (copied) as the cell divides. A brief outline of the basic steps
involved in gene cloning are:
i.
Isolation of desired DNA fragment by using restriction enzymes
ii.
Insertion of the DNA fragment into a suitable vector (Plasmid) to
make rDNA
iii.
Transfer of rDNA into bacterial host cell (Transformation)
iv.
Selection and multiplication of recombinant host cell to get a
clone
v.
Expression of cloned gene in host cell.
Using this strategy
several enzymes, hormones and vaccines can be produced
Related Topics