Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 20 : Breeding and Biotechnology
Animal Breeding
Animal
Breeding
A breed is a
group of animals of common origin within a species that has certain
distinguishing characters that are not found in other members of the same
species like general appearance and others striking features.
Breeding involves mating parents
of different varieties each having some desired trait which are passed
onto the offspring.
Objectives of Animal Breeding
Animal breeding aims at improving the
genotypes of domesticated animals to increase their yield and improve the
desirable qualities to produce milk, egg and meat.
When breeding takes
place between animals of the same breed, it is called inbreeding. The
cross between different breeds is called outbreeding.
1. Inbreeding
Inbreeding refers to the
mating of closely related animals within the same breed for about
4-6 generations. Superior males and superior females of the same breed are
identified and mated in pairs. It helps in the accumulation of superior genes
and elimination of genes which are undesirable.
Hissardale is a new breed of sheep
developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri (Magra) ewes and Australian Marino
rams.
Inbreeding depression: Continued inbreeding reduces
fertility and productivity. Inbreeding exposes harmful recessive genes that are
eliminated by selection.
2. Outbreeding
It is the breeding of
unrelated animals. The offsprings formed are called hybrids. The hybrids
are stronger and vigorous than their parents. Cross between two
different species with desirable features of economic value are mated. Let’s
see what cross produce a mule.
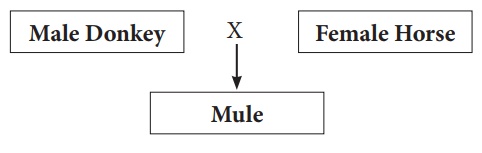
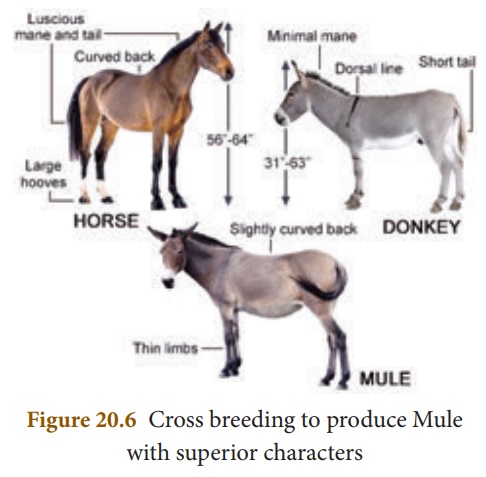
Mule is superior to
horse in strength, intelligence, ability to work and resistance to diseases but
they are sterile.
3. Heterosis
The superiority of the
hybrid obtained by cross breeding is called as heterosis or hybrid
vigour.
Effects of hybrid vigour in animal breeding
·
Increased production of milk by cattle
·
Increased production of egg by poultry
·
High quality of meat is produced
·
Increased growth rate in domesticated animals
Related Topics